Safe Reinforcement Learning with Dual Robustness
Paper and Code
Sep 13, 2023
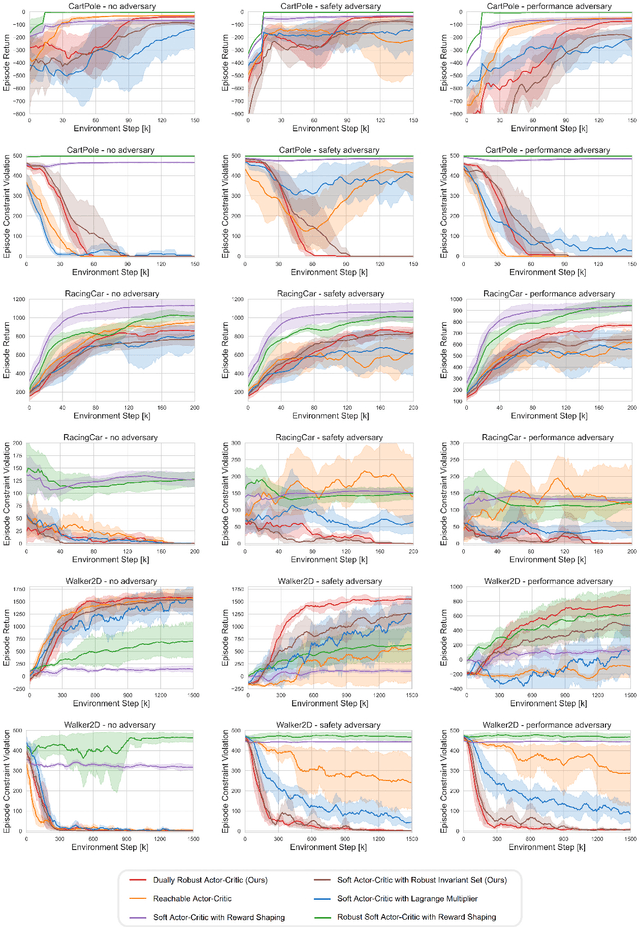
Reinforcement learning (RL) agents are vulnerable to adversarial disturbances, which can deteriorate task performance or compromise safety specifications. Existing methods either address safety requirements under the assumption of no adversary (e.g., safe RL) or only focus on robustness against performance adversaries (e.g., robust RL). Learning one policy that is both safe and robust remains a challenging open problem. The difficulty is how to tackle two intertwined aspects in the worst cases: feasibility and optimality. Optimality is only valid inside a feasible region, while identification of maximal feasible region must rely on learning the optimal policy. To address this issue, we propose a systematic framework to unify safe RL and robust RL, including problem formulation, iteration scheme, convergence analysis and practical algorithm design. This unification is built upon constrained two-player zero-sum Markov games. A dual policy iteration scheme is proposed, which simultaneously optimizes a task policy and a safety policy. The convergence of this iteration scheme is proved. Furthermore, we design a deep RL algorithm for practical implementation, called dually robust actor-critic (DRAC). The evaluations with safety-critical benchmarks demonstrate that DRAC achieves high performance and persistent safety under all scenarios (no adversary, safety adversary, performance adversary), outperforming all baselines significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge