Robot Motion Planning as Video Prediction: A Spatio-Temporal Neural Network-based Motion Planner
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2022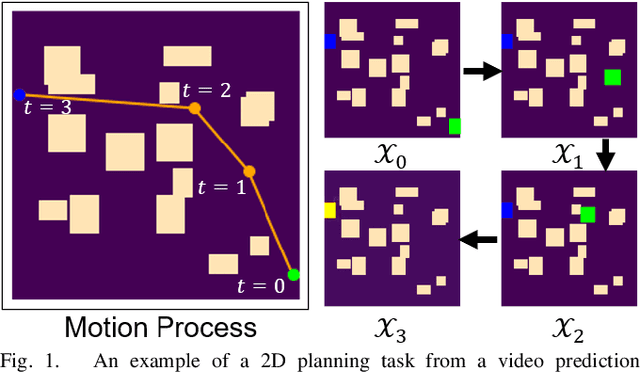
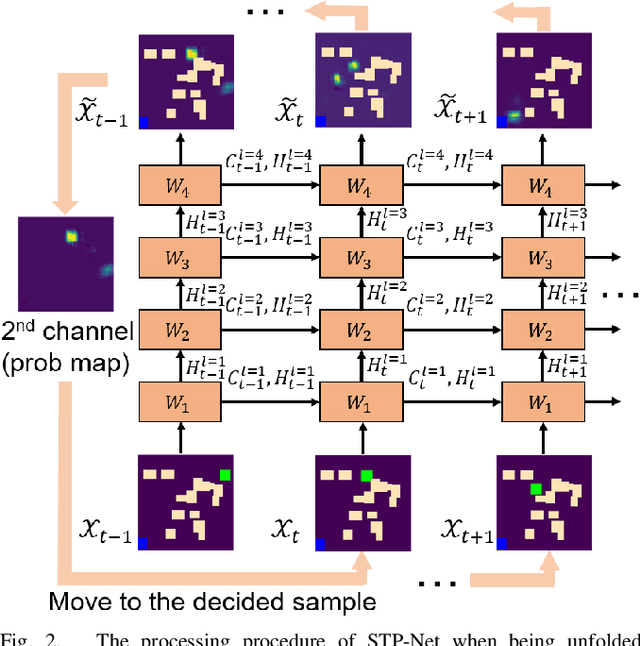
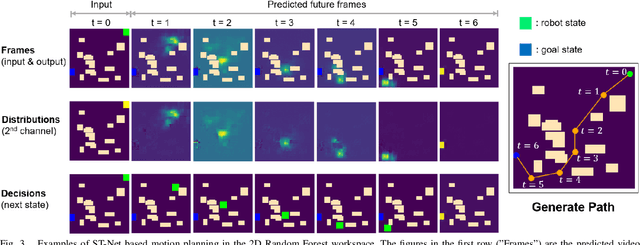
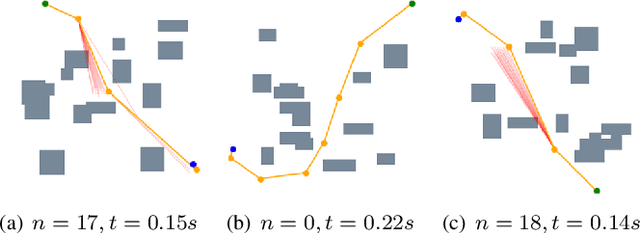
Neural network (NN)-based methods have emerged as an attractive approach for robot motion planning due to strong learning capabilities of NN models and their inherently high parallelism. Despite the current development in this direction, the efficient capture and processing of important sequential and spatial information, in a direct and simultaneous way, is still relatively under-explored. To overcome the challenge and unlock the potentials of neural networks for motion planning tasks, in this paper, we propose STP-Net, an end-to-end learning framework that can fully extract and leverage important spatio-temporal information to form an efficient neural motion planner. By interpreting the movement of the robot as a video clip, robot motion planning is transformed to a video prediction task that can be performed by STP-Net in both spatially and temporally efficient ways. Empirical evaluations across different seen and unseen environments show that, with nearly 100% accuracy (aka, success rate), STP-Net demonstrates very promising performance with respect to both planning speed and path cost. Compared with existing NN-based motion planners, STP-Net achieves at least 5x, 2.6x and 1.8x faster speed with lower path cost on 2D Random Forest, 2D Maze and 3D Random Forest environments, respectively. Furthermore, STP-Net can quickly and simultaneously compute multiple near-optimal paths in multi-robot motion planning tasks
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge