Rigid and non-rigid motion compensation in weight-bearing cone-beam CT of the knee using inertial measurements
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2021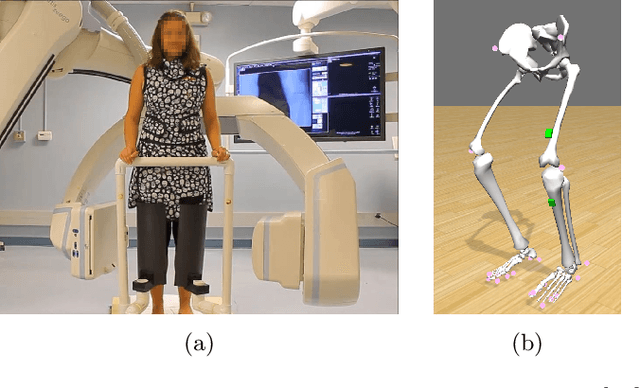
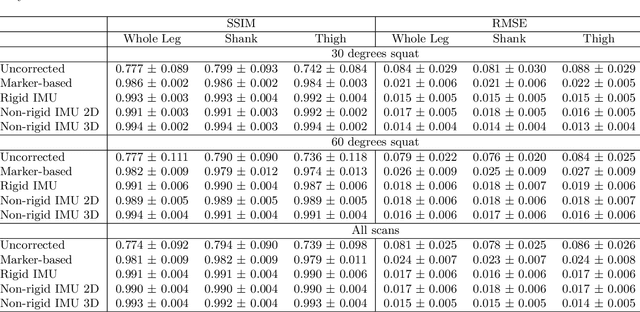
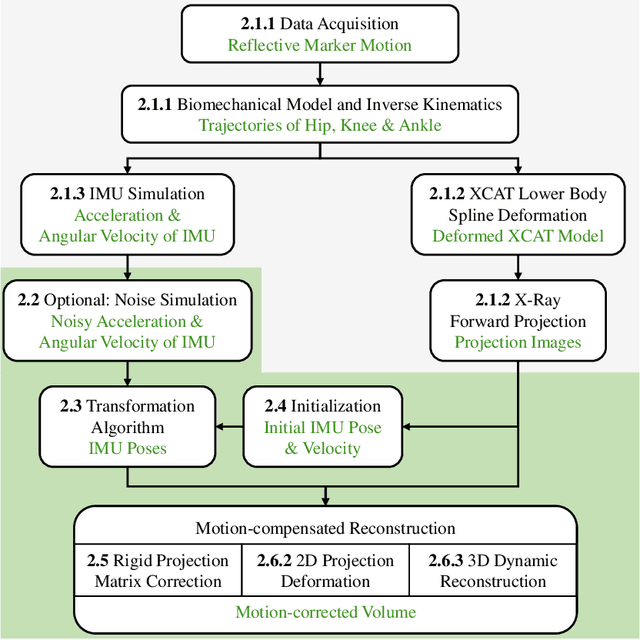
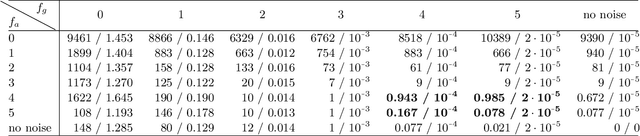
Involuntary subject motion is the main source of artifacts in weight-bearing cone-beam CT of the knee. To achieve image quality for clinical diagnosis, the motion needs to be compensated. We propose to use inertial measurement units (IMUs) attached to the leg for motion estimation. We perform a simulation study using real motion recorded with an optical tracking system. Three IMU-based correction approaches are evaluated, namely rigid motion correction, non-rigid 2D projection deformation and non-rigid 3D dynamic reconstruction. We present an initialization process based on the system geometry. With an IMU noise simulation, we investigate the applicability of the proposed methods in real applications. All proposed IMU-based approaches correct motion at least as good as a state-of-the-art marker-based approach. The structural similarity index and the root mean squared error between motion-free and motion corrected volumes are improved by 24-35% and 78-85%, respectively, compared with the uncorrected case. The noise analysis shows that the noise levels of commercially available IMUs need to be improved by a factor of $10^5$ which is currently only achieved by specialized hardware not robust enough for the application. The presented study confirms the feasibility of this novel approach and defines improvements necessary for a real application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge