Rethinking Perceptual Metrics for Medical Image Translation
Paper and Code
Apr 10, 2024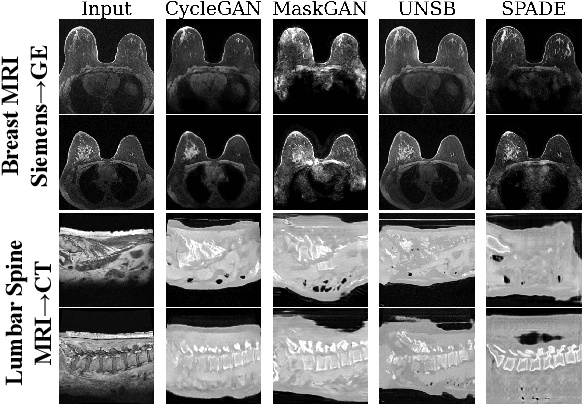
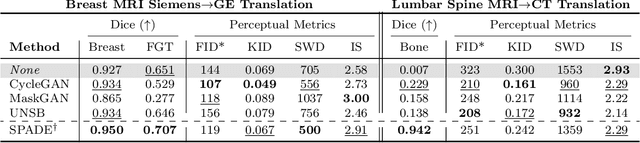
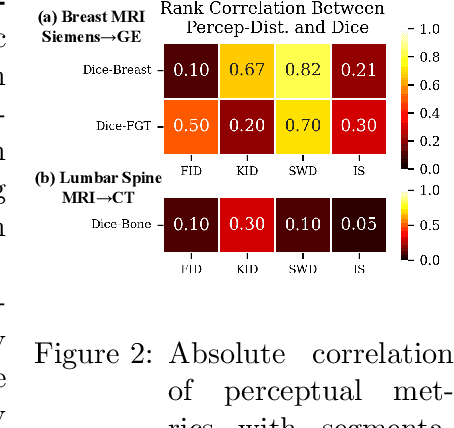
Modern medical image translation methods use generative models for tasks such as the conversion of CT images to MRI. Evaluating these methods typically relies on some chosen downstream task in the target domain, such as segmentation. On the other hand, task-agnostic metrics are attractive, such as the network feature-based perceptual metrics (e.g., FID) that are common to image translation in general computer vision. In this paper, we investigate evaluation metrics for medical image translation on two medical image translation tasks (GE breast MRI to Siemens breast MRI and lumbar spine MRI to CT), tested on various state-of-the-art translation methods. We show that perceptual metrics do not generally correlate with segmentation metrics due to them extending poorly to the anatomical constraints of this sub-field, with FID being especially inconsistent. However, we find that the lesser-used pixel-level SWD metric may be useful for subtle intra-modality translation. Our results demonstrate the need for further research into helpful metrics for medical image translation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge