REST: Debiased Social Recommendation via Reconstructing Exposure Strategies
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2022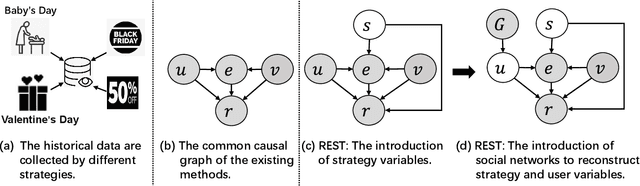
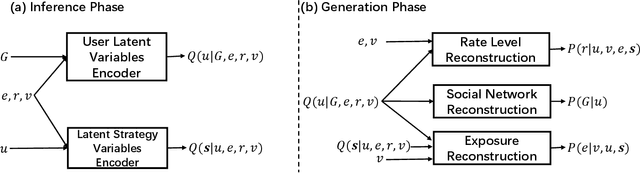
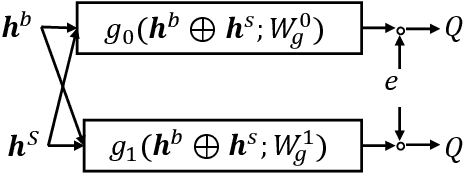
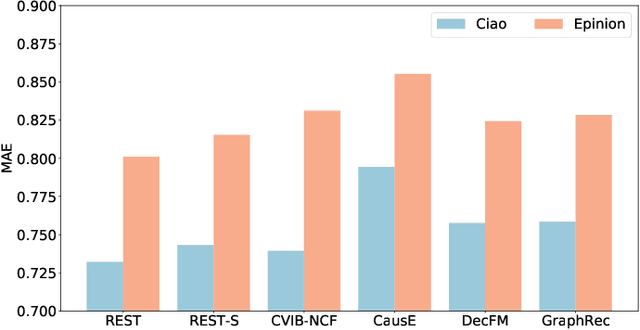
The recommendation system, relying on historical observational data to model the complex relationships among the users and items, has achieved great success in real-world applications. Selection bias is one of the most important issues of the existing observational data based approaches, which is actually caused by multiple types of unobserved exposure strategies (e.g. promotions and holiday effects). Though various methods have been proposed to address this problem, they are mainly relying on the implicit debiasing techniques but not explicitly modeling the unobserved exposure strategies. By explicitly Reconstructing Exposure STrategies (REST in short), we formalize the recommendation problem as the counterfactual reasoning and propose the debiased social recommendation method. In REST, we assume that the exposure of an item is controlled by the latent exposure strategies, the user, and the item. Based on the above generation process, we first provide the theoretical guarantee of our method via identification analysis. Second, we employ a variational auto-encoder to reconstruct the latent exposure strategies, with the help of the social networks and the items. Third, we devise a counterfactual reasoning based recommendation algorithm by leveraging the recovered exposure strategies. Experiments on four real-world datasets, including three published datasets and one private WeChat Official Account dataset, demonstrate significant improvements over several state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge