Recipe for a General, Powerful, Scalable Graph Transformer
Paper and Code
May 25, 2022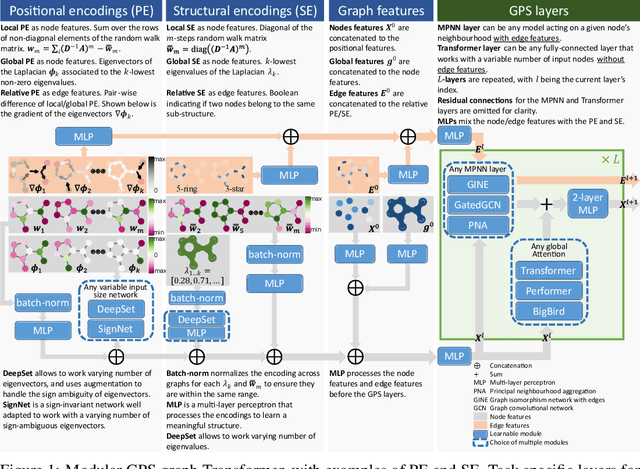
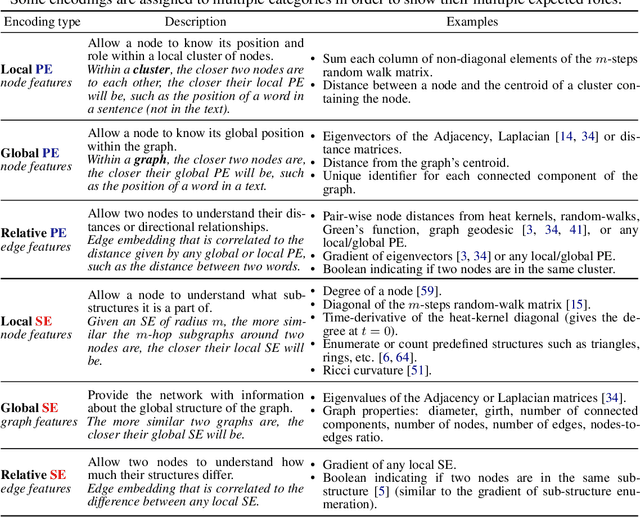
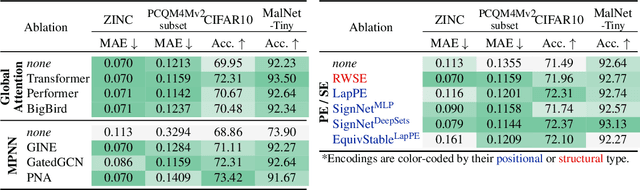
We propose a recipe on how to build a general, powerful, scalable (GPS) graph Transformer with linear complexity and state-of-the-art results on a diverse set of benchmarks. Graph Transformers (GTs) have gained popularity in the field of graph representation learning with a variety of recent publications but they lack a common foundation about what constitutes a good positional or structural encoding, and what differentiates them. In this paper, we summarize the different types of encodings with a clearer definition and categorize them as being $\textit{local}$, $\textit{global}$ or $\textit{relative}$. Further, GTs remain constrained to small graphs with few hundred nodes, and we propose the first architecture with a complexity linear to the number of nodes and edges $O(N+E)$ by decoupling the local real-edge aggregation from the fully-connected Transformer. We argue that this decoupling does not negatively affect the expressivity, with our architecture being a universal function approximator for graphs. Our GPS recipe consists of choosing 3 main ingredients: (i) positional/structural encoding, (ii) local message-passing mechanism, and (iii) global attention mechanism. We build and open-source a modular framework $\textit{GraphGPS}$ that supports multiple types of encodings and that provides efficiency and scalability both in small and large graphs. We test our architecture on 11 benchmarks and show very competitive results on all of them, show-casing the empirical benefits gained by the modularity and the combination of different strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge