Quad-networks: unsupervised learning to rank for interest point detection
Paper and Code
Apr 10, 2017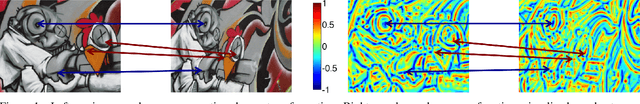
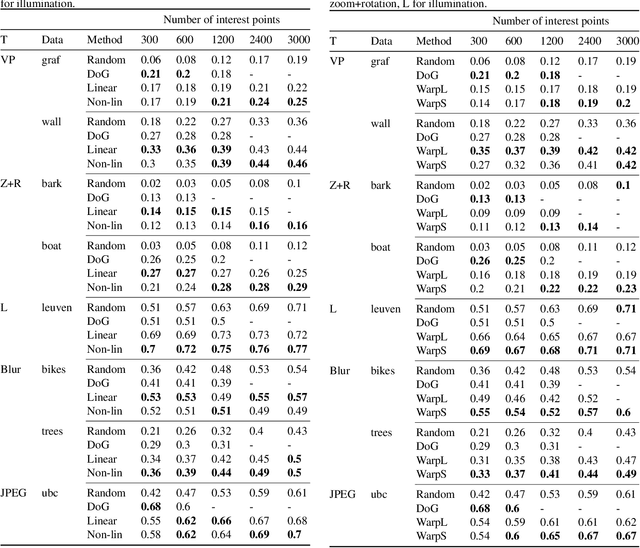
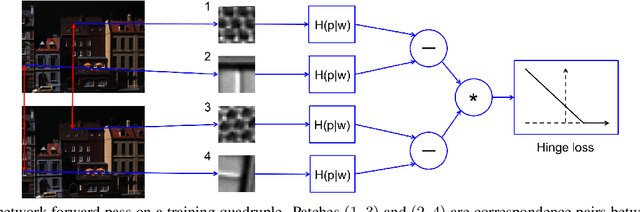
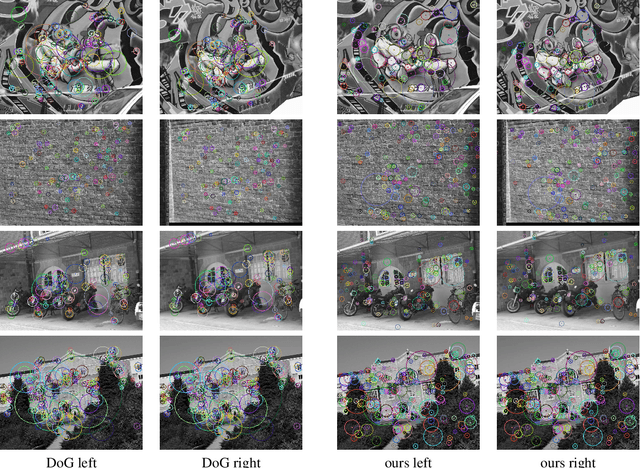
Several machine learning tasks require to represent the data using only a sparse set of interest points. An ideal detector is able to find the corresponding interest points even if the data undergo a transformation typical for a given domain. Since the task is of high practical interest in computer vision, many hand-crafted solutions were proposed. In this paper, we ask a fundamental question: can we learn such detectors from scratch? Since it is often unclear what points are "interesting", human labelling cannot be used to find a truly unbiased solution. Therefore, the task requires an unsupervised formulation. We are the first to propose such a formulation: training a neural network to rank points in a transformation-invariant manner. Interest points are then extracted from the top/bottom quantiles of this ranking. We validate our approach on two tasks: standard RGB image interest point detection and challenging cross-modal interest point detection between RGB and depth images. We quantitatively show that our unsupervised method performs better or on-par with baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge