Pushing the right boundaries matters! Wasserstein Adversarial Training for Label Noise
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2019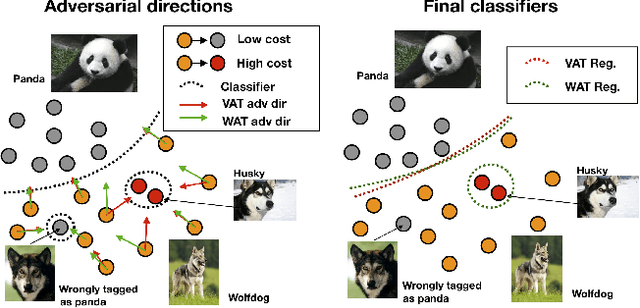
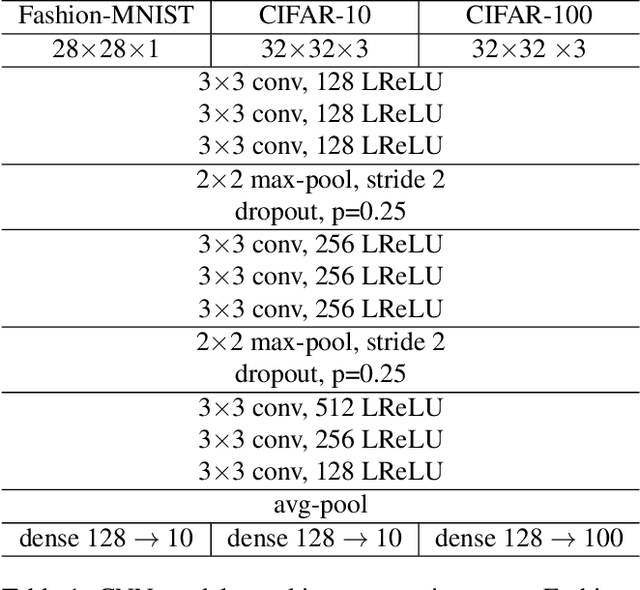
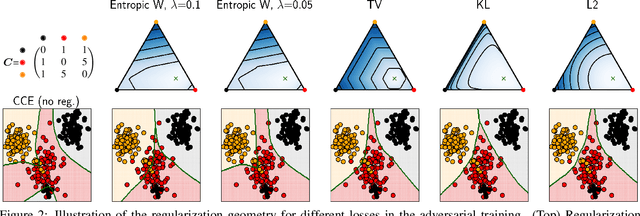
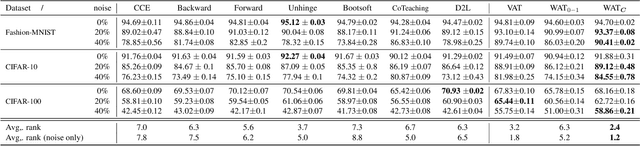
Noisy labels often occur in vision datasets, especially when they are issued from crowdsourcing or Web scraping. In this paper, we propose a new regularization method which enables one to learn robust classifiers in presence of noisy data. To achieve this goal, we augment the virtual adversarial loss with a Wasserstein distance. This distance allows us to take into account specific relations between classes by leveraging on the geometric properties of this optimal transport distance. Notably, we encode the class similarities in the ground cost that is used to compute the Wasserstein distance. As a consequence, we can promote smoothness between classes that are very dissimilar, while keeping the classification decision function sufficiently complex for similar classes. While designing this ground cost can be left as a problem-specific modeling task, we show in this paper that using the semantic relations between classes names already leads to good results.Our proposed Wasserstein Adversarial Training (WAT) outperforms state of the art on four datasets corrupted with noisy labels: three classical benchmarks and one real case in remote sensing image semantic segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge