Protein Representation Learning with Sequence Information Embedding: Does it Always Lead to a Better Performance?
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2024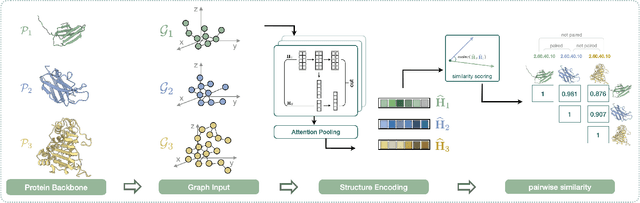
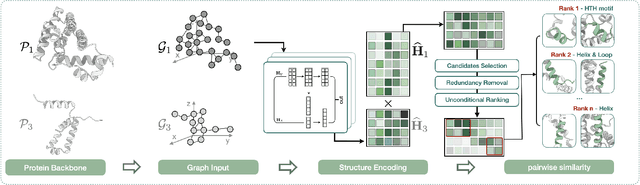

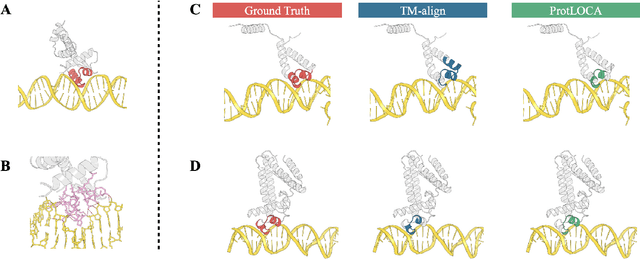
Deep learning has become a crucial tool in studying proteins. While the significance of modeling protein structure has been discussed extensively in the literature, amino acid types are typically included in the input as a default operation for many inference tasks. This study demonstrates with structure alignment task that embedding amino acid types in some cases may not help a deep learning model learn better representation. To this end, we propose ProtLOCA, a local geometry alignment method based solely on amino acid structure representation. The effectiveness of ProtLOCA is examined by a global structure-matching task on protein pairs with an independent test dataset based on CATH labels. Our method outperforms existing sequence- and structure-based representation learning methods by more quickly and accurately matching structurally consistent protein domains. Furthermore, in local structure pairing tasks, ProtLOCA for the first time provides a valid solution to highlight common local structures among proteins with different overall structures but the same function. This suggests a new possibility for using deep learning methods to analyze protein structure to infer function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge