Probable Domain Generalization via Quantile Risk Minimization
Paper and Code
Jul 20, 2022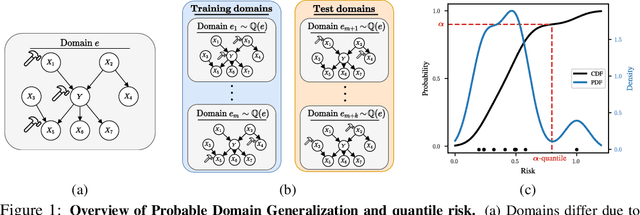
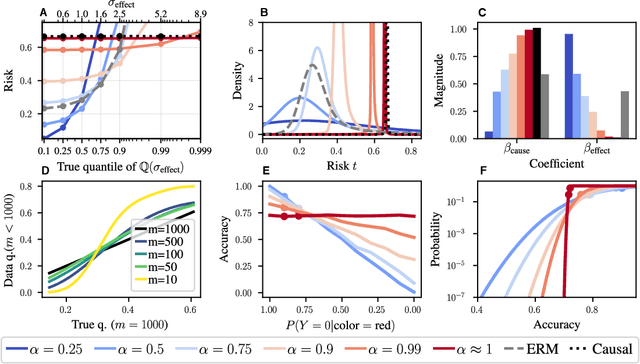
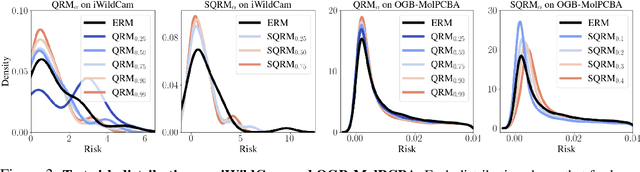
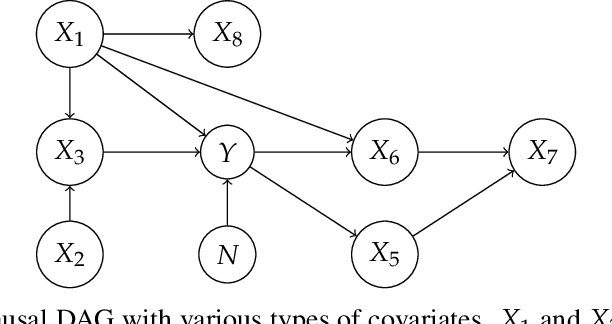
Domain generalization (DG) seeks predictors which perform well on unseen test distributions by leveraging labeled training data from multiple related distributions or domains. To achieve this, the standard formulation optimizes for worst-case performance over the set of all possible domains. However, with worst-case shifts very unlikely in practice, this generally leads to overly-conservative solutions. In fact, a recent study found that no DG algorithm outperformed empirical risk minimization in terms of average performance. In this work, we argue that DG is neither a worst-case problem nor an average-case problem, but rather a probabilistic one. To this end, we propose a probabilistic framework for DG, which we call Probable Domain Generalization, wherein our key idea is that distribution shifts seen during training should inform us of probable shifts at test time. To realize this, we explicitly relate training and test domains as draws from the same underlying meta-distribution, and propose a new optimization problem -- Quantile Risk Minimization (QRM) -- which requires that predictors generalize with high probability. We then prove that QRM: (i) produces predictors that generalize to new domains with a desired probability, given sufficiently many domains and samples; and (ii) recovers the causal predictor as the desired probability of generalization approaches one. In our experiments, we introduce a more holistic quantile-focused evaluation protocol for DG, and show that our algorithms outperform state-of-the-art baselines on real and synthetic data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge