Performance Limits for Signals of Opportunity-Based Navigation
Paper and Code
Jul 23, 2024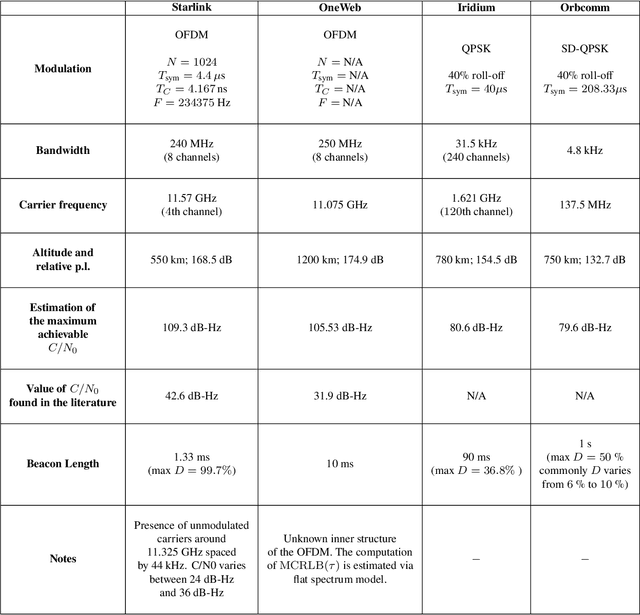
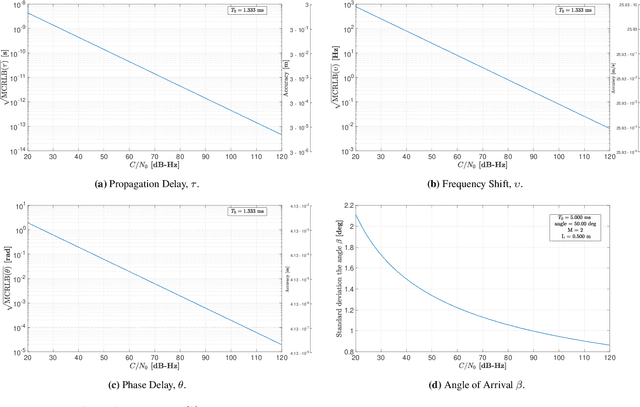
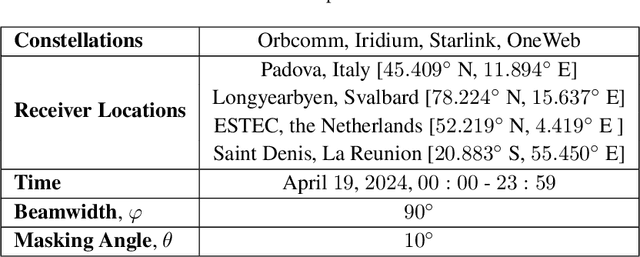
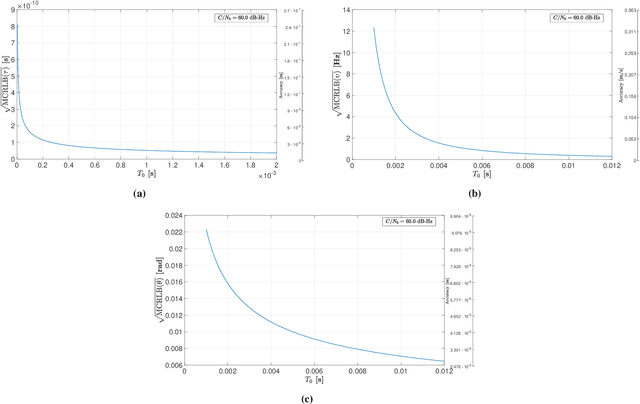
This paper investigates the potential of non-terrestrial and terrestrial signals of opportunity (SOOP) for navigation applications. Non-terrestrial SOOP analysis employs modified Cram\`er-Rao lower bound (MCRLB) to establish a relationship between SOOP characteristics and the accuracy of ranging information. This approach evaluates hybrid navigation module performance without direct signal simulation. The MCRLB is computed for ranging accuracy, considering factors like propagation delay, frequency offset, phase offset, and angle-of-arrival (AOA), across diverse non-terrestrial SOOP candidates. Additionally, Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP) and low earth orbit (LEO) SOOP availability are assessed. Validation involves comparing MCRLB predictions with actual ranging measurements obtained in a realistic simulated scenario. Furthermore, a qualitative evaluation examines terrestrial SOOP, considering signal availability, accuracy attainability, and infrastructure demands.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge