PASS: Peer-Agreement based Sample Selection for training with Noisy Labels
Paper and Code
Mar 20, 2023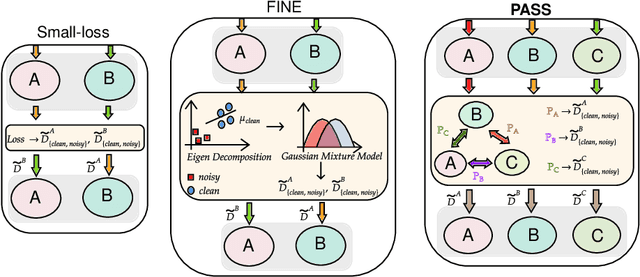
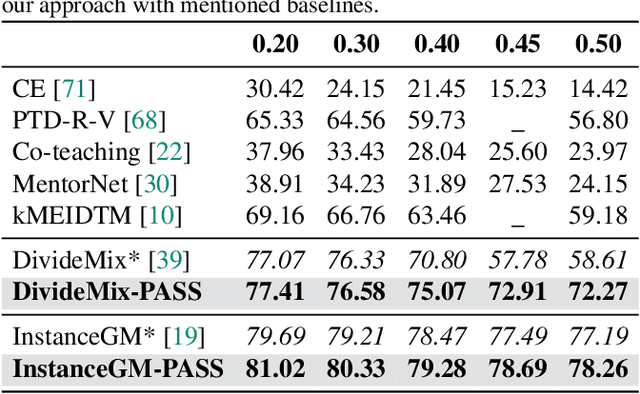


Noisy labels present a significant challenge in deep learning because models are prone to overfitting. This problem has driven the development of sophisticated techniques to address the issue, with one critical component being the selection of clean and noisy label samples. Selecting noisy label samples is commonly based on the small-loss hypothesis or on feature-based sampling, but we present empirical evidence that shows that both strategies struggle to differentiate between noisy label and hard samples, resulting in relatively large proportions of samples falsely selected as clean. To address this limitation, we propose a novel peer-agreement based sample selection (PASS). An automated thresholding technique is then applied to the agreement score to select clean and noisy label samples. PASS is designed to be easily integrated into existing noisy label robust frameworks, and it involves training a set of classifiers in a round-robin fashion, with peer models used for sample selection. In the experiments, we integrate our PASS with several state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, including InstanceGM, DivideMix, SSR, FaMUS, AugDesc, and C2D, and evaluate their effectiveness on several noisy label benchmark datasets, such as CIFAR-100, CIFAR-N, Animal-10N, Red Mini-Imagenet, Clothing1M, Mini-Webvision, and Imagenet. Our results demonstrate that our new sample selection approach improves the existing SOTA results of algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge