ParaLBench: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Computational Paralinguistics over Acoustic Foundation Models
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2024
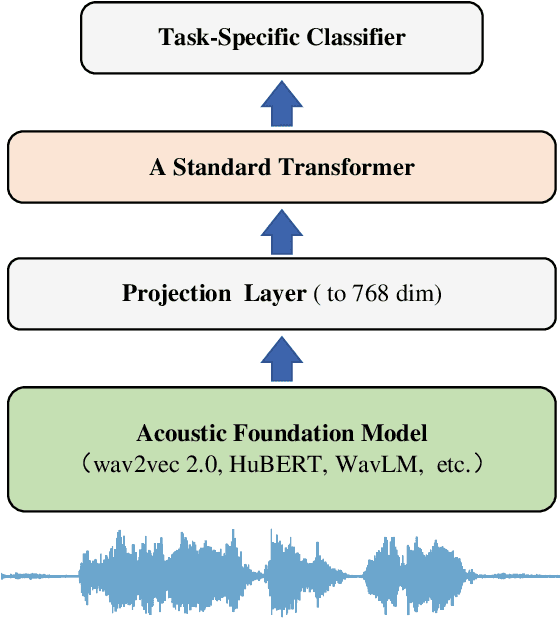
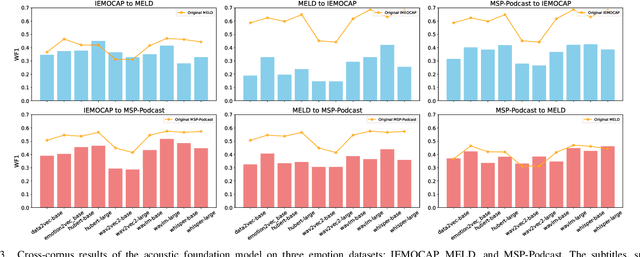
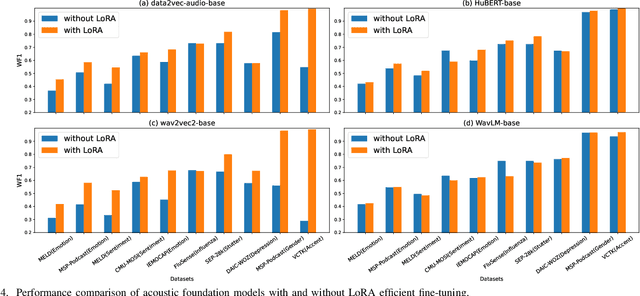
Computational paralinguistics (ComParal) aims to develop algorithms and models to automatically detect, analyze, and interpret non-verbal information from speech communication, e. g., emotion, health state, age, and gender. Despite its rapid progress, it heavily depends on sophisticatedly designed models given specific paralinguistic tasks. Thus, the heterogeneity and diversity of ComParal models largely prevent the realistic implementation of ComParal models. Recently, with the advent of acoustic foundation models because of self-supervised learning, developing more generic models that can efficiently perceive a plethora of paralinguistic information has become an active topic in speech processing. However, it lacks a unified evaluation framework for a fair and consistent performance comparison. To bridge this gap, we conduct a large-scale benchmark, namely ParaLBench, which concentrates on standardizing the evaluation process of diverse paralinguistic tasks, including critical aspects of affective computing such as emotion recognition and emotion dimensions prediction, over different acoustic foundation models. This benchmark contains ten datasets with thirteen distinct paralinguistic tasks, covering short-, medium- and long-term characteristics. Each task is carried out on 14 acoustic foundation models under a unified evaluation framework, which allows for an unbiased methodological comparison and offers a grounded reference for the ComParal community. Based on the insights gained from ParaLBench, we also point out potential research directions, i.e., the cross-corpus generalizability, to propel ComParal research in the future. The code associated with this study will be available to foster the transparency and replicability of this work for succeeding researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge