Opposite Structure Learning for Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Feb 06, 2020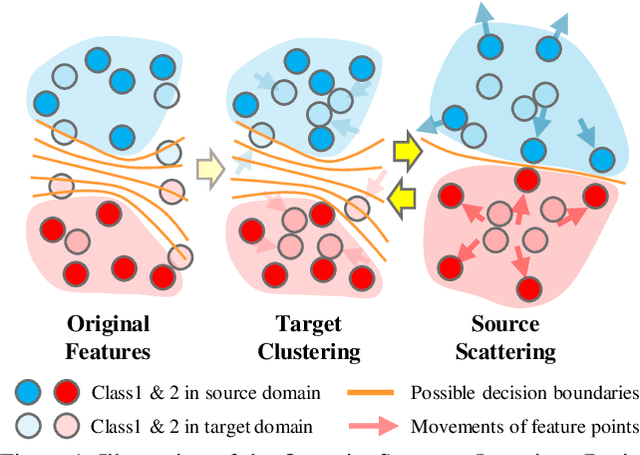

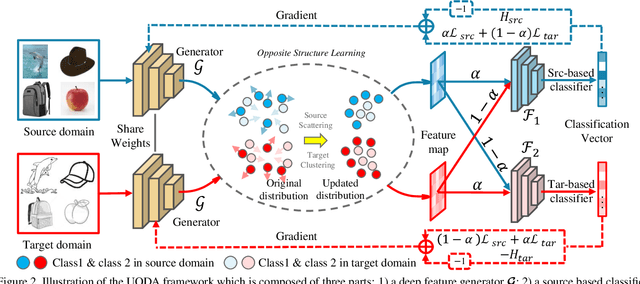

Current adversarial adaptation methods attempt to align the cross-domain features whereas two challenges remain unsolved: 1) conditional distribution mismatch between different domains and 2) the bias of decision boundary towards the source domain. To solve these challenges, we propose a novel framework for semi-supervised domain adaptation by unifying the learning of opposite structures (UODA). UODA consists of a generator and two classifiers (i.e., the source-based and the target-based classifiers respectively) which are trained with opposite forms of losses for a unified object. The target-based classifier attempts to cluster the target features to improve intra-class density and enlarge inter-class divergence. Meanwhile, the source-based classifier is designed to scatter the source features to enhance the smoothness of decision boundary. Through the alternation of source-feature expansion and target-feature clustering procedures, the target features are well-enclosed within the dilated boundary of the corresponding source features. This strategy effectively makes the cross-domain features precisely aligned. To overcome the model collapse through training, we progressively update the measurement of distance and the feature representation on both domains via an adversarial training paradigm. Extensive experiments on the benchmarks of DomainNet and Office-home datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach over the state-of-the-art method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge