On the Limits of Evaluating Embodied Agent Model Generalization Using Validation Sets
Paper and Code
May 18, 2022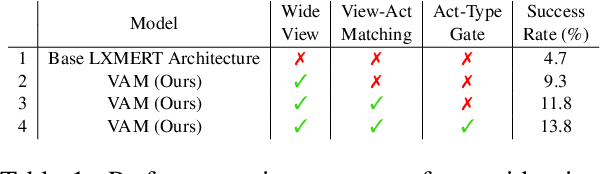
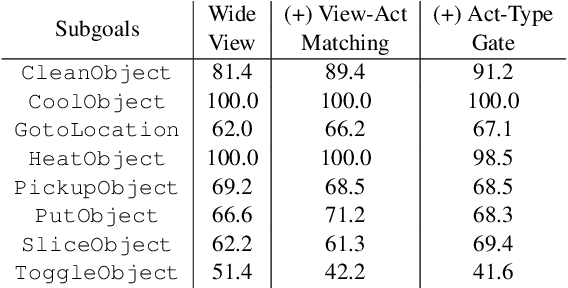
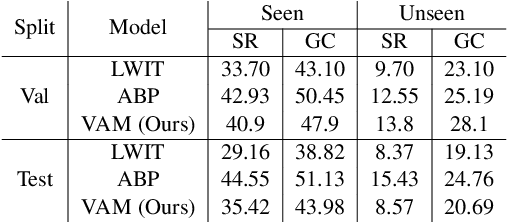
Natural language guided embodied task completion is a challenging problem since it requires understanding natural language instructions, aligning them with egocentric visual observations, and choosing appropriate actions to execute in the environment to produce desired changes. We experiment with augmenting a transformer model for this task with modules that effectively utilize a wider field of view and learn to choose whether the next step requires a navigation or manipulation action. We observed that the proposed modules resulted in improved, and in fact state-of-the-art performance on an unseen validation set of a popular benchmark dataset, ALFRED. However, our best model selected using the unseen validation set underperforms on the unseen test split of ALFRED, indicating that performance on the unseen validation set may not in itself be a sufficient indicator of whether model improvements generalize to unseen test sets. We highlight this result as we believe it may be a wider phenomenon in machine learning tasks but primarily noticeable only in benchmarks that limit evaluations on test splits, and highlights the need to modify benchmark design to better account for variance in model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge