On the Effectiveness of Sampled Softmax Loss for Item Recommendation
Paper and Code
Jan 07, 2022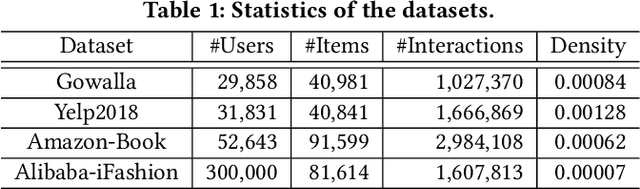

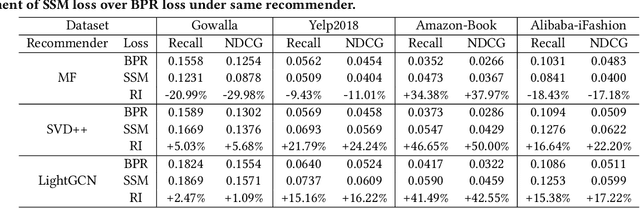
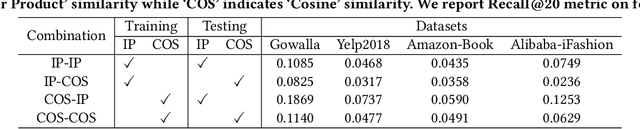
Learning objectives of recommender models remain largely unexplored. Most methods routinely adopt either pointwise or pairwise loss to train the model parameters, while rarely pay attention to softmax loss due to the high computational cost. Sampled softmax loss emerges as an efficient substitute for softmax loss. Its special case, InfoNCE loss, has been widely used in self-supervised learning and exhibited remarkable performance for contrastive learning. Nonetheless, limited studies use sampled softmax loss as the learning objective to train the recommender. Worse still, none of them explore its properties and answer "Does sampled softmax loss suit for item recommendation?" and "What are the conceptual advantages of sampled softmax loss, as compared with the prevalent losses?", to the best of our knowledge. In this work, we aim to better understand sampled softmax loss for item recommendation. Specifically, we first theoretically reveal three model-agnostic advantages: (1) mitigating popularity bias, which is beneficial to long-tail recommendation; (2) mining hard negative samples, which offers informative gradients to optimize model parameters; and (3) maximizing the ranking metric, which facilitates top-K performance. Moreover, we probe the model-specific characteristics on the top of various recommenders. Experimental results suggest that sampled softmax loss is more friendly to history and graph-based recommenders (e.g., SVD++ and LightGCN), but performs poorly for ID-based models (e.g., MF). We ascribe this to its shortcoming in learning representation magnitude, making the combination with the models that are also incapable of adjusting representation magnitude learn poor representations. In contrast, the history- and graph-based models, which naturally adjust representation magnitude according to node degree, are able to compensate for the shortcoming of sampled softmax loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge