On Inferring User Socioeconomic Status with Mobility Records
Paper and Code
Nov 15, 2022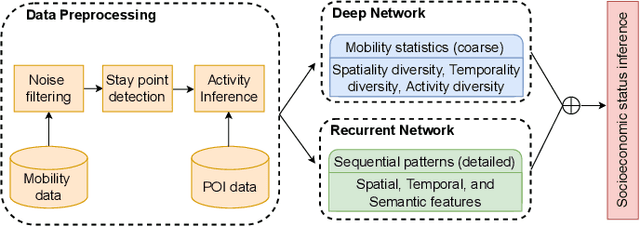
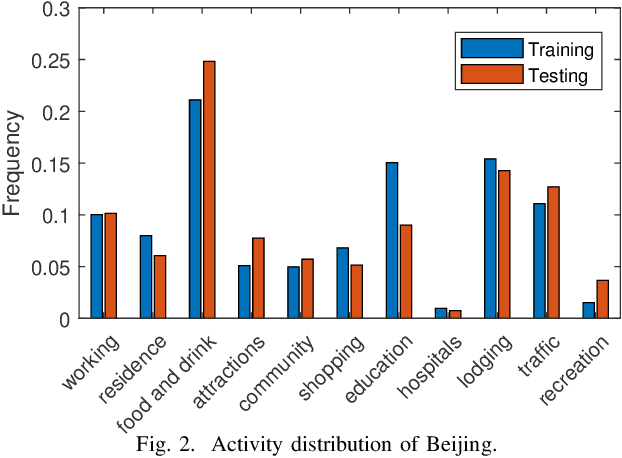
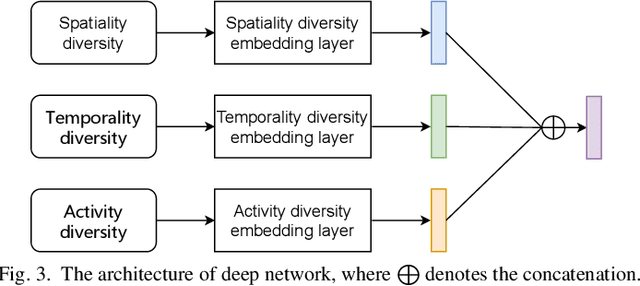
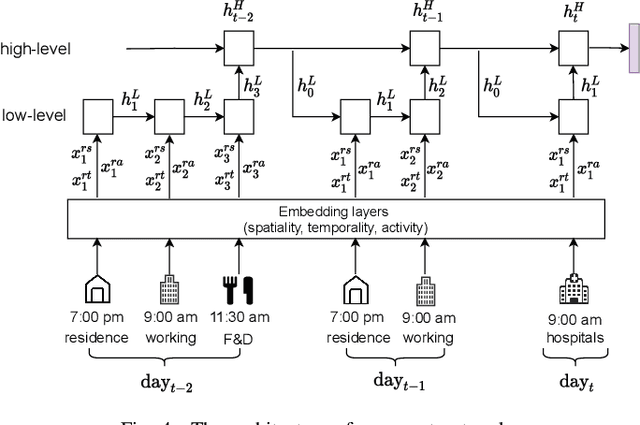
When users move in a physical space (e.g., an urban space), they would have some records called mobility records (e.g., trajectories) generated by devices such as mobile phones and GPS devices. Naturally, mobility records capture essential information of how users work, live and entertain in their daily lives, and therefore, they have been used in a wide range of tasks such as user profile inference, mobility prediction and traffic management. In this paper, we expand this line of research by investigating the problem of inferring user socioeconomic statuses (such as prices of users' living houses as a proxy of users' socioeconomic statuses) based on their mobility records, which can potentially be used in real-life applications such as the car loan business. For this task, we propose a socioeconomic-aware deep model called DeepSEI. The DeepSEI model incorporates two networks called deep network and recurrent network, which extract the features of the mobility records from three aspects, namely spatiality, temporality and activity, one at a coarse level and the other at a detailed level. We conduct extensive experiments on real mobility records data, POI data and house prices data. The results verify that the DeepSEI model achieves superior performance than existing studies. All datasets used in this paper will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge