Noise-Aware Saliency Prediction for Videos with Incomplete Gaze Data
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2021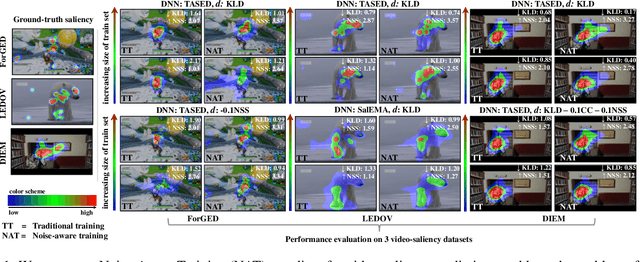
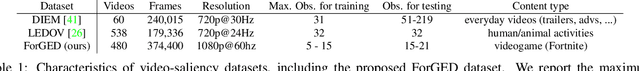
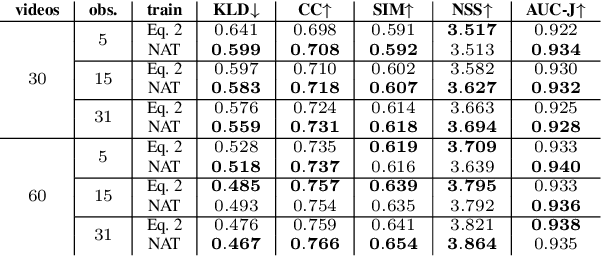

Deep-learning-based algorithms have led to impressive results in visual-saliency prediction, but the impact of noise in training gaze data has been largely overlooked. This issue is especially relevant for videos, where the gaze data tends to be incomplete, and thus noisier, compared to images. Therefore, we propose a noise-aware training (NAT) paradigm for visual-saliency prediction that quantifies the uncertainty arising from gaze data incompleteness and inaccuracy, and accounts for it in training. We demonstrate the advantage of NAT independently of the adopted model architecture, loss function, or training dataset. Given its robustness to the noise in incomplete training datasets, NAT ushers in the possibility of designing gaze datasets with fewer human subjects. We also introduce the first dataset that offers a video-game context for video-saliency research, with rich temporal semantics, and multiple gaze attractors per frame.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge