Neuromorphic Hardware learns to learn
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2019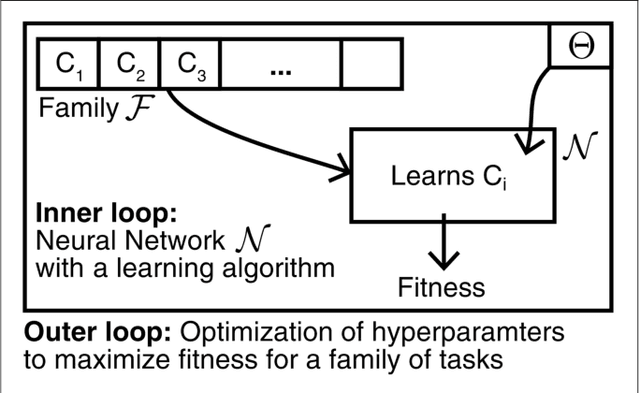
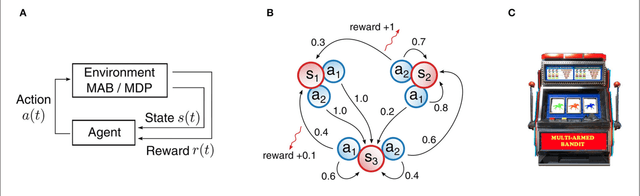
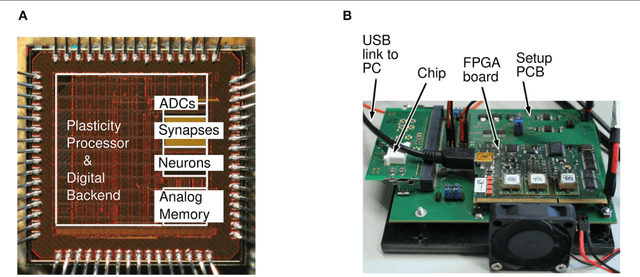
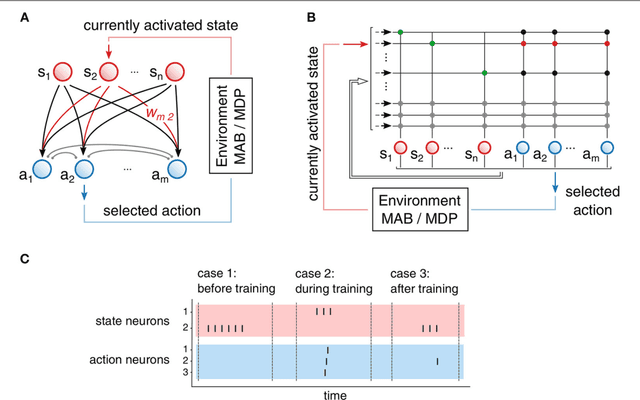
Hyperparameters and learning algorithms for neuromorphic hardware are usually chosen by hand. In contrast, the hyperparameters and learning algorithms of networks of neurons in the brain, which they aim to emulate, have been optimized through extensive evolutionary and developmental processes for specific ranges of computing and learning tasks. Occasionally this process has been emulated through genetic algorithms, but these require themselves hand-design of their details and tend to provide a limited range of improvements. We employ instead other powerful gradient-free optimization tools, such as cross-entropy methods and evolutionary strategies, in order to port the function of biological optimization processes to neuromorphic hardware. As an example, we show that this method produces neuromorphic agents that learn very efficiently from rewards. In particular, meta-plasticity, i.e., the optimization of the learning rule which they use, substantially enhances reward-based learning capability of the hardware. In addition, we demonstrate for the first time Learning-to-Learn benefits from such hardware, in particular, the capability to extract abstract knowledge from prior learning experiences that speeds up the learning of new but related tasks. Learning-to-Learn is especially suited for accelerated neuromorphic hardware, since it makes it feasible to carry out the required very large number of network computations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge