Neural Check-Worthiness Ranking with Weak Supervision: Finding Sentences for Fact-Checking
Paper and Code
Mar 20, 2019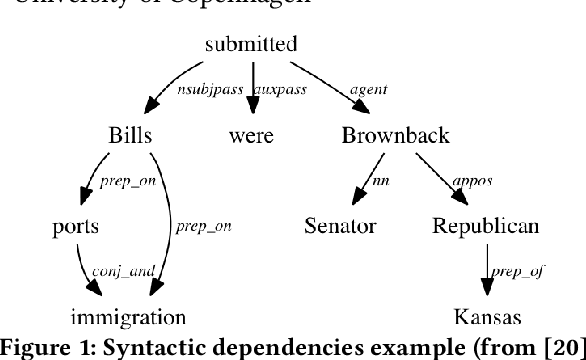
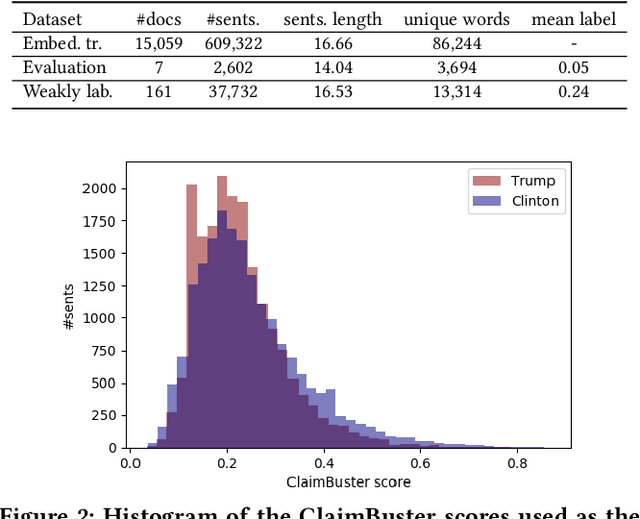
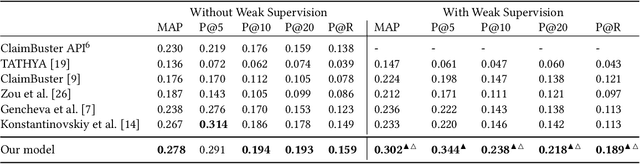
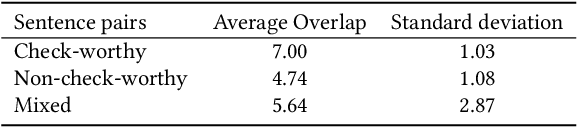
Automatic fact-checking systems detect misinformation, such as fake news, by (i) selecting check-worthy sentences for fact-checking, (ii) gathering related information to the sentences, and (iii) inferring the factuality of the sentences. Most prior research on (i) uses hand-crafted features to select check-worthy sentences, and does not explicitly account for the recent finding that the top weighted terms in both check-worthy and non-check-worthy sentences are actually overlapping [15]. Motivated by this, we present a neural check-worthiness sentence ranking model that represents each word in a sentence by \textit{both} its embedding (aiming to capture its semantics) and its syntactic dependencies (aiming to capture its role in modifying the semantics of other terms in the sentence). Our model is an end-to-end trainable neural network for check-worthiness ranking, which is trained on large amounts of unlabelled data through weak supervision. Thorough experimental evaluation against state of the art baselines, with and without weak supervision, shows our model to be superior at all times (+13% in MAP and +28% at various Precision cut-offs from the best baseline with statistical significance). Empirical analysis of the use of weak supervision, word embedding pretraining on domain-specific data, and the use of syntactic dependencies of our model reveals that check-worthy sentences contain notably more identical syntactic dependencies than non-check-worthy sentences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge