Neural Architecture Search From Fréchet Task Distance
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2021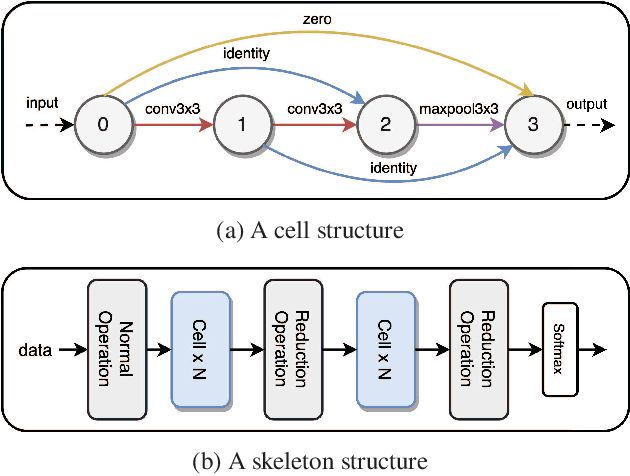

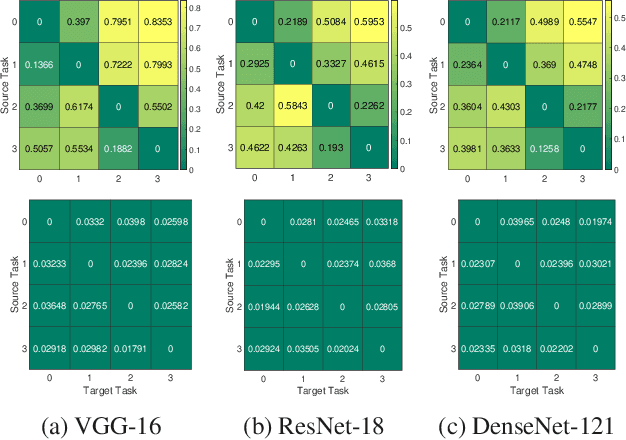

We formulate a Fr\'echet-type asymmetric distance between tasks based on Fisher Information Matrices. We show how the distance between a target task and each task in a given set of baseline tasks can be used to reduce the neural architecture search space for the target task. The complexity reduction in search space for task-specific architectures is achieved by building on the optimized architectures for similar tasks instead of doing a full search without using this side information. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach and its improvements over the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge