N2C2: Nearest Neighbor Enhanced Confidence Calibration for Cross-Lingual In-Context Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 12, 2025
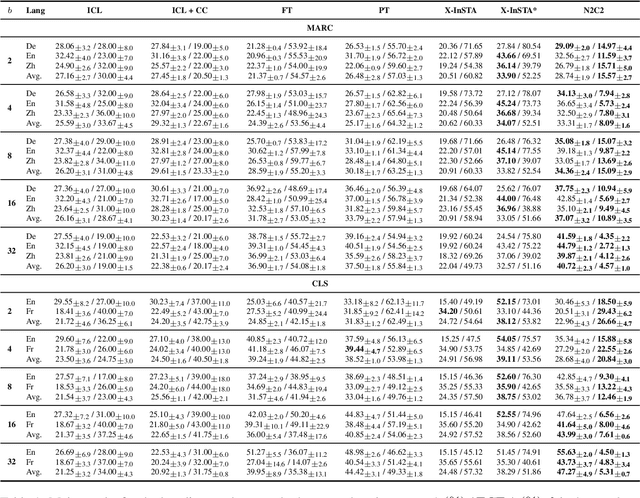
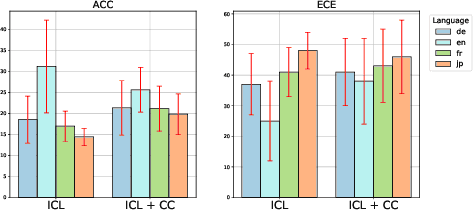
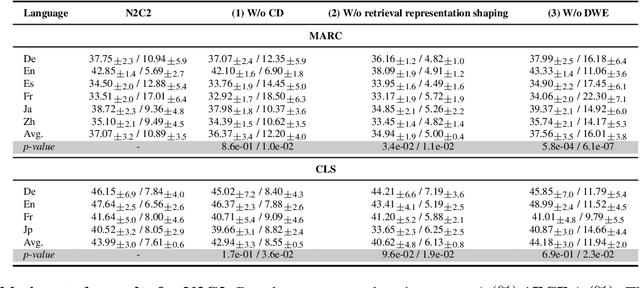
Recent advancements of in-context learning (ICL) show language models can significantly improve their performance when demonstrations are provided. However, little attention has been paid to model calibration and prediction confidence of ICL in cross-lingual scenarios. To bridge this gap, we conduct a thorough analysis of ICL for cross-lingual sentiment classification. Our findings suggest that ICL performs poorly in cross-lingual scenarios, exhibiting low accuracy and presenting high calibration errors. In response, we propose a novel approach, N2C2, which employs a -nearest neighbors augmented classifier for prediction confidence calibration. N2C2 narrows the prediction gap by leveraging a datastore of cached few-shot instances. Specifically, N2C2 integrates the predictions from the datastore and incorporates confidence-aware distribution, semantically consistent retrieval representation, and adaptive neighbor combination modules to effectively utilize the limited number of supporting instances. Evaluation on two multilingual sentiment classification datasets demonstrates that N2C2 outperforms traditional ICL. It surpasses fine tuning, prompt tuning and recent state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and calibration errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge