Mutual Graph Learning for Camouflaged Object Detection
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2021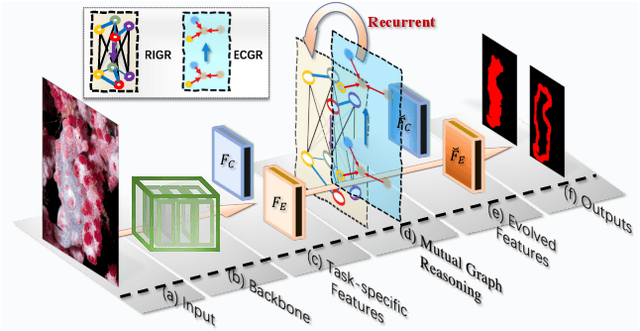
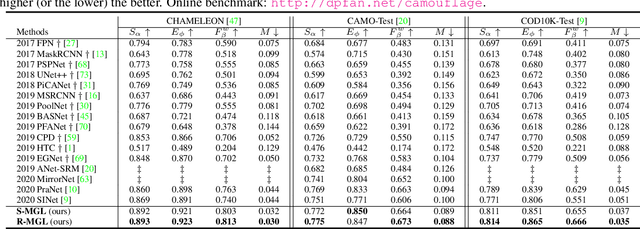
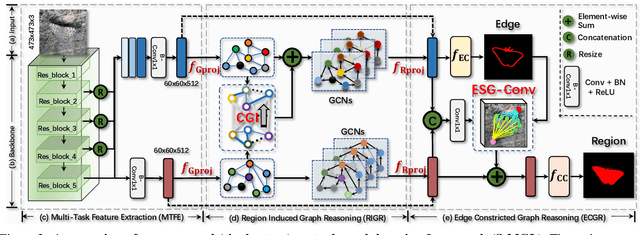
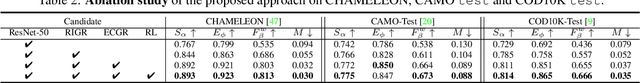
Automatically detecting/segmenting object(s) that blend in with their surroundings is difficult for current models. A major challenge is that the intrinsic similarities between such foreground objects and background surroundings make the features extracted by deep model indistinguishable. To overcome this challenge, an ideal model should be able to seek valuable, extra clues from the given scene and incorporate them into a joint learning framework for representation co-enhancement. With this inspiration, we design a novel Mutual Graph Learning (MGL) model, which generalizes the idea of conventional mutual learning from regular grids to the graph domain. Specifically, MGL decouples an image into two task-specific feature maps -- one for roughly locating the target and the other for accurately capturing its boundary details -- and fully exploits the mutual benefits by recurrently reasoning their high-order relations through graphs. Importantly, in contrast to most mutual learning approaches that use a shared function to model all between-task interactions, MGL is equipped with typed functions for handling different complementary relations to maximize information interactions. Experiments on challenging datasets, including CHAMELEON, CAMO and COD10K, demonstrate the effectiveness of our MGL with superior performance to existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge