MRI quantification of liver fibrosis using diamagnetic susceptibility: An ex-vivo feasibility study
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2024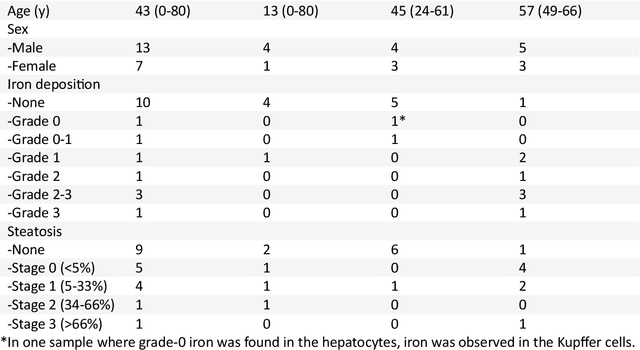
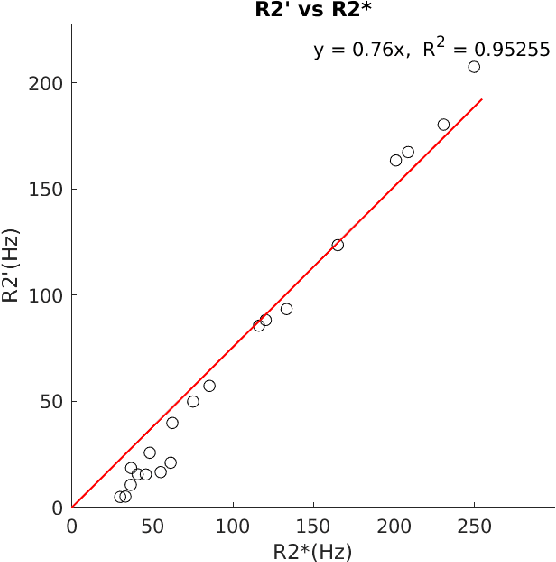
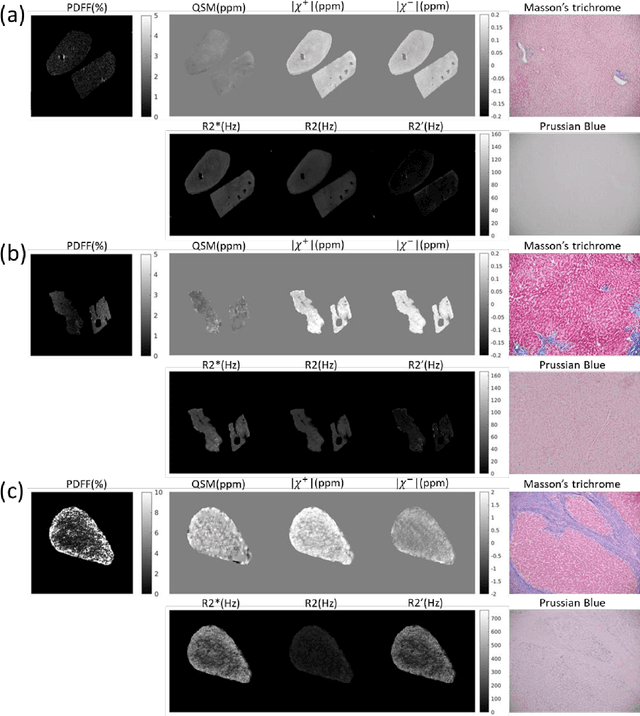
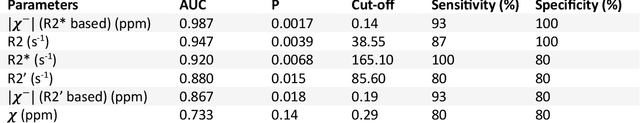
In chronic liver disease, liver fibrosis develops as excessive deposition of extracellular matrix macromolecules, predominantly collagens, progressively form fibrous scars that disrupt the hepatic architecture, and fibrosis, iron, and fat are interrelated. Fibrosis is the best predictor of morbidity and mortality in chronic liver disease but liver biopsy, the reference method for diagnosis and staging, is invasive and limited by sampling and interobserver variability and risks of complications. The overall objective of this study was to develop a new non-invasive method to quantify fibrosis using diamagnetic susceptibility sources with histology validation in ex vivo liver explants.
* 17 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge