MoTe: Learning Motion-Text Diffusion Model for Multiple Generation Tasks
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2024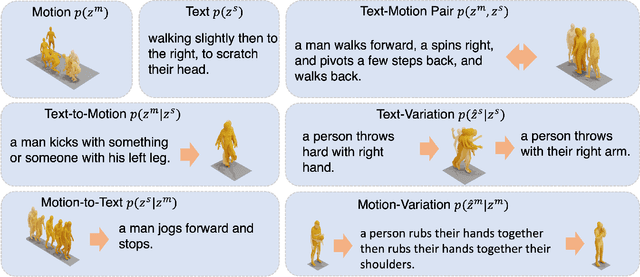

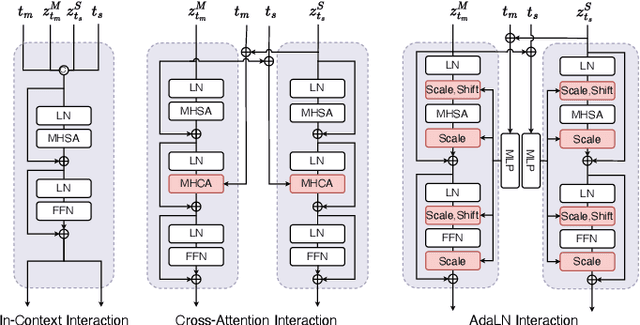

Recently, human motion analysis has experienced great improvement due to inspiring generative models such as the denoising diffusion model and large language model. While the existing approaches mainly focus on generating motions with textual descriptions and overlook the reciprocal task. In this paper, we present~\textbf{MoTe}, a unified multi-modal model that could handle diverse tasks by learning the marginal, conditional, and joint distributions of motion and text simultaneously. MoTe enables us to handle the paired text-motion generation, motion captioning, and text-driven motion generation by simply modifying the input context. Specifically, MoTe is composed of three components: Motion Encoder-Decoder (MED), Text Encoder-Decoder (TED), and Moti-on-Text Diffusion Model (MTDM). In particular, MED and TED are trained for extracting latent embeddings, and subsequently reconstructing the motion sequences and textual descriptions from the extracted embeddings, respectively. MTDM, on the other hand, performs an iterative denoising process on the input context to handle diverse tasks. Experimental results on the benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method on text-to-motion generation and competitive performance on motion captioning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge