MMD Aggregated Two-Sample Test
Paper and Code
Oct 28, 2021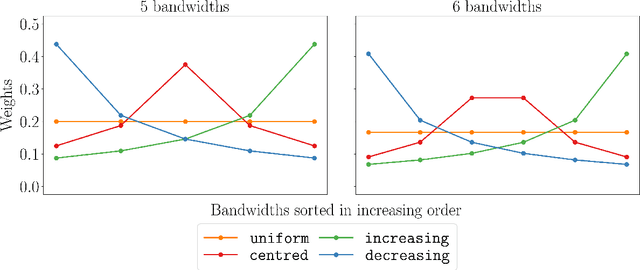
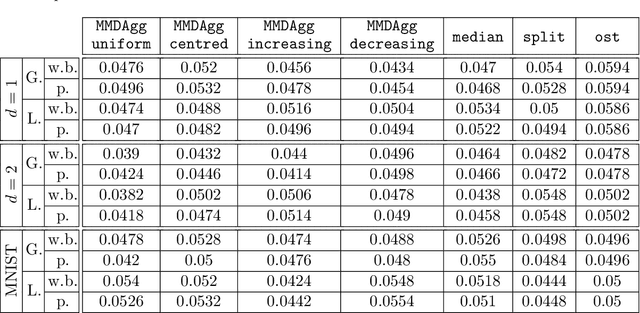
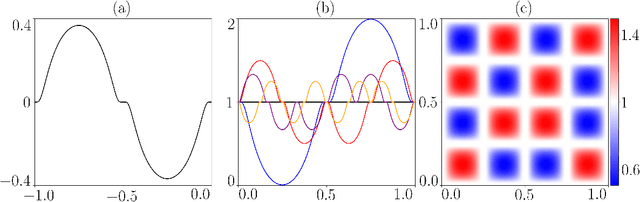
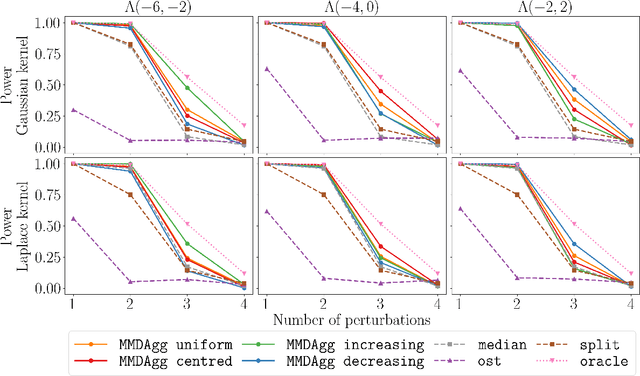
We propose a novel nonparametric two-sample test based on the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD), which is constructed by aggregating tests with different kernel bandwidths. This aggregation procedure, called MMDAgg, ensures that test power is maximised over the collection of kernels used, without requiring held-out data for kernel selection (which results in a loss of test power), or arbitrary kernel choices such as the median heuristic. We work in the non-asymptotic framework, and prove that our aggregated test is minimax adaptive over Sobolev balls. Our guarantees are not restricted to a specific kernel, but hold for any product of one-dimensional translation invariant characteristic kernels which are absolutely and square integrable. Moreover, our results apply for popular numerical procedures to determine the test threshold, namely permutations and the wild bootstrap. Through numerical experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets, we demonstrate that MMDAgg outperforms alternative state-of-the-art approaches to MMD kernel adaptation for two-sample testing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge