ML-BPM: Multi-teacher Learning with Bidirectional Photometric Mixing for Open Compound Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2022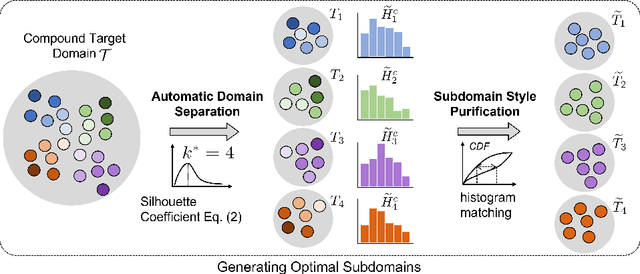
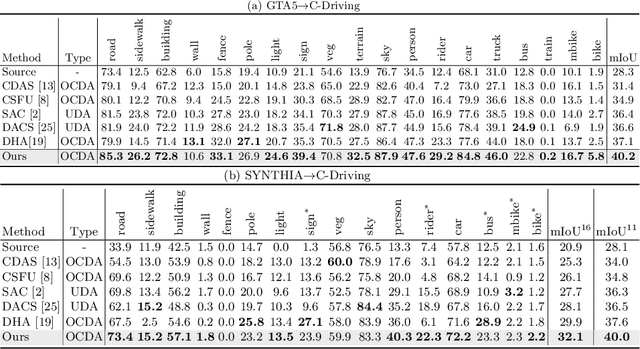

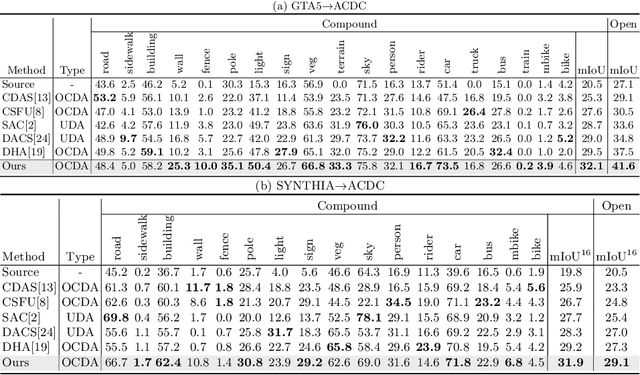
Open compound domain adaptation (OCDA) considers the target domain as the compound of multiple unknown homogeneous subdomains. The goal of OCDA is to minimize the domain gap between the labeled source domain and the unlabeled compound target domain, which benefits the model generalization to the unseen domains. Current OCDA for semantic segmentation methods adopt manual domain separation and employ a single model to simultaneously adapt to all the target subdomains. However, adapting to a target subdomain might hinder the model from adapting to other dissimilar target subdomains, which leads to limited performance. In this work, we introduce a multi-teacher framework with bidirectional photometric mixing to separately adapt to every target subdomain. First, we present an automatic domain separation to find the optimal number of subdomains. On this basis, we propose a multi-teacher framework in which each teacher model uses bidirectional photometric mixing to adapt to one target subdomain. Furthermore, we conduct an adaptive distillation to learn a student model and apply consistency regularization to improve the student generalization. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show the efficacy of the proposed approach for both the compound domain and the open domains against existing state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge