Mitigating the Language Mismatch and Repetition Issues in LLM-based Machine Translation via Model Editing
Paper and Code
Oct 09, 2024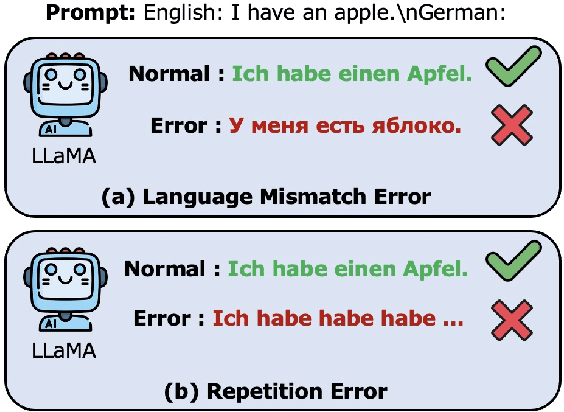

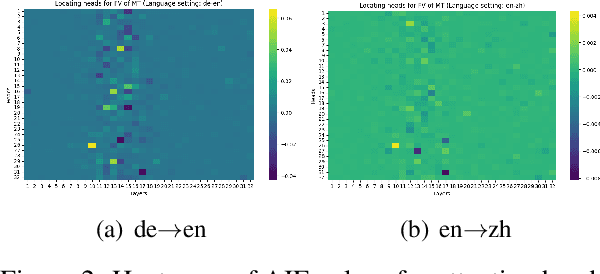

Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently revolutionized the NLP field, while they still fall short in some specific down-stream tasks. In the work, we focus on utilizing LLMs to perform machine translation, where we observe that two patterns of errors frequently occur and drastically affect the translation quality: language mismatch and repetition. The work sets out to explore the potential for mitigating these two issues by leveraging model editing methods, e.g., by locating Feed-Forward Network (FFN) neurons or something that are responsible for the errors and deactivating them in the inference time. We find that directly applying such methods either limited effect on the targeted errors or has significant negative side-effect on the general translation quality, indicating that the located components may also be crucial for ensuring machine translation with LLMs on the rails. To this end, we propose to refine the located components by fetching the intersection of the locating results under different language settings, filtering out the aforementioned information that is irrelevant to targeted errors. The experiment results empirically demonstrate that our methods can effectively reduce the language mismatch and repetition ratios and meanwhile enhance or keep the general translation quality in most cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge