Mitigating Annotation Artifacts in Natural Language Inference Datasets to Improve Cross-dataset Generalization Ability
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2019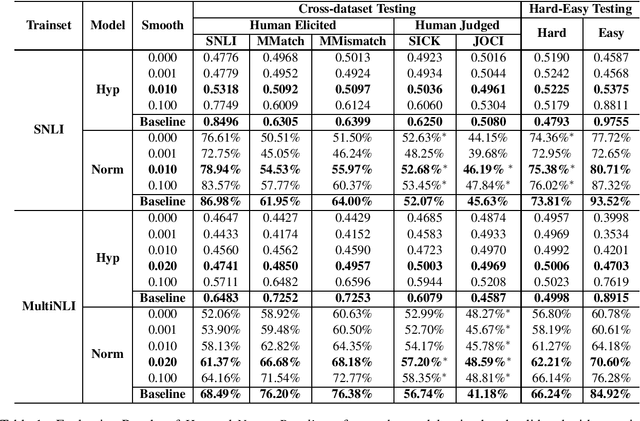
Natural language inference (NLI) aims at predicting the relationship between a given pair of premise and hypothesis. However, several works have found that there widely exists a bias pattern called annotation artifacts in NLI datasets, making it possible to identify the label only by looking at the hypothesis. This irregularity makes the evaluation results over-estimated and affects models' generalization ability. In this paper, we consider a more trust-worthy setting, i.e., cross-dataset evaluation. We explore the impacts of annotation artifacts in cross-dataset testing. Furthermore, we propose a training framework to mitigate the impacts of the bias pattern. Experimental results demonstrate that our methods can alleviate the negative effect of the artifacts and improve the generalization ability of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge