Misinfo Belief Frames: A Case Study on Covid & Climate News
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2021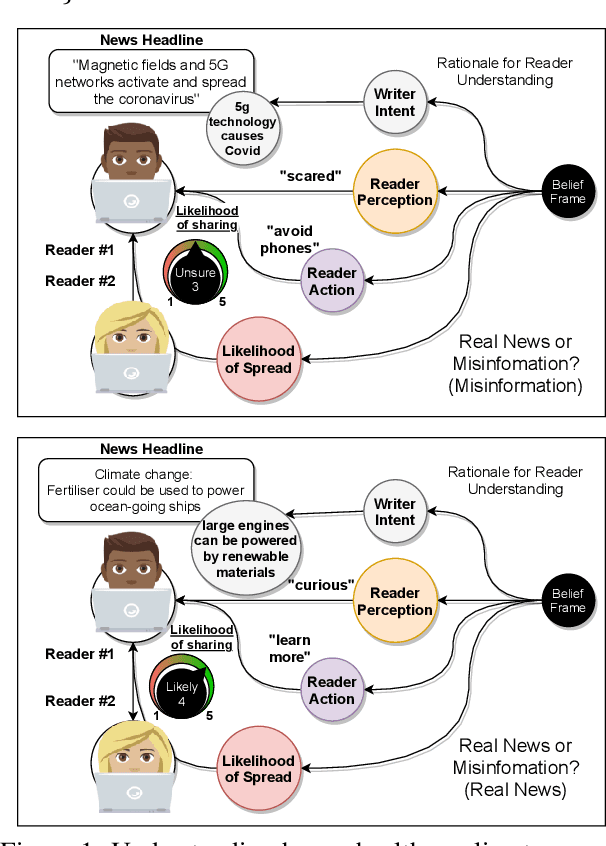
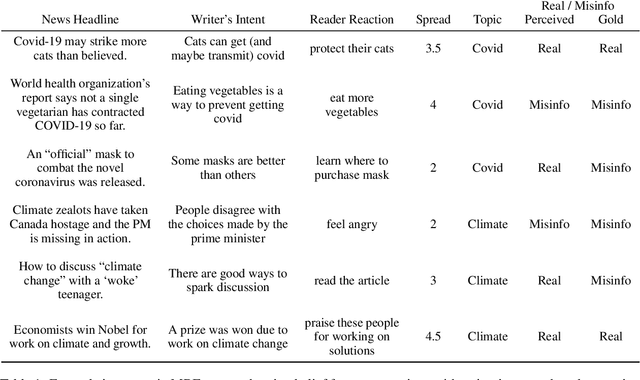

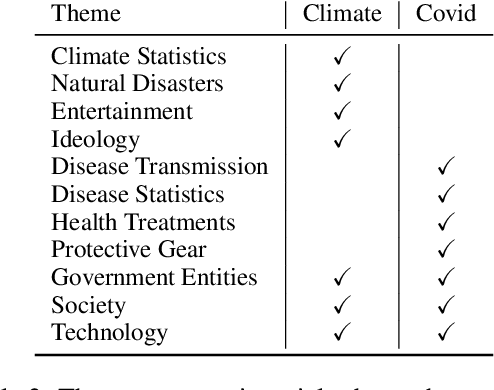
Prior beliefs of readers impact the way in which they project meaning onto news headlines. These beliefs can influence their perception of news reliability, as well as their reaction to news, and their likelihood of spreading the misinformation through social networks. However, most prior work focuses on fact-checking veracity of news or stylometry rather than measuring impact of misinformation. We propose Misinfo Belief Frames, a formalism for understanding how readers perceive the reliability of news and the impact of misinformation. We also introduce the Misinfo Belief Frames (MBF) corpus, a dataset of 66k inferences over 23.5k headlines. Misinformation frames use commonsense reasoning to uncover implications of real and fake news headlines focused on global crises: the Covid-19 pandemic and climate change. Our results using large-scale language modeling to predict misinformation frames show that machine-generated inferences can influence readers' trust in news headlines (readers' trust in news headlines was affected in 29.3% of cases). This demonstrates the potential effectiveness of using generated frames to counter misinformation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge