MILIOM: Tightly Coupled Multi-Input Lidar-Inertia Odometry and Mapping
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2021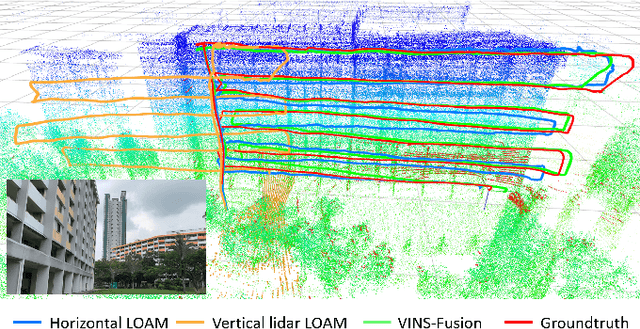
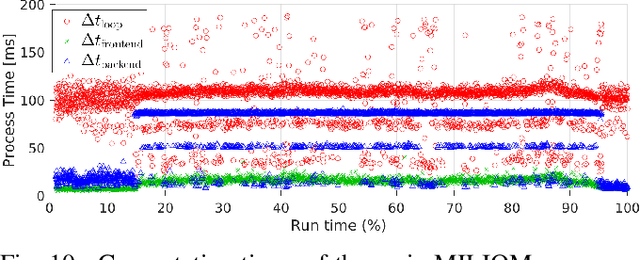
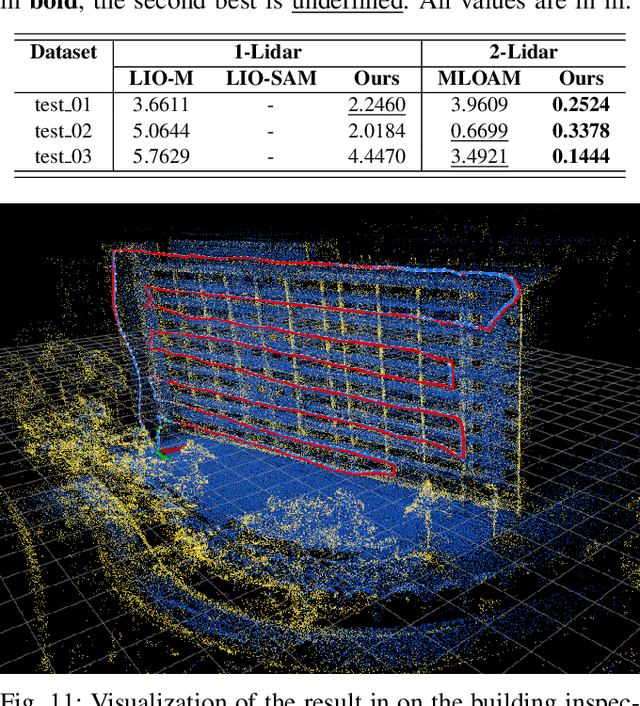
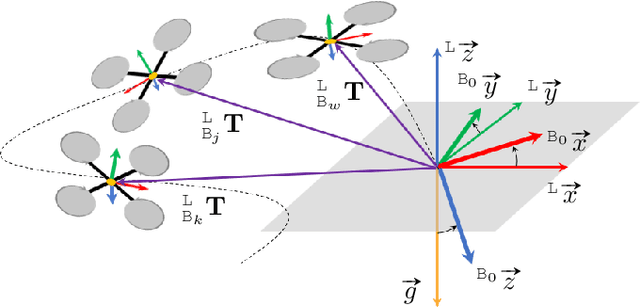
In this paper we investigate a tightly coupled Lidar-Inertia Odometry and Mapping (LIOM) scheme, with the capability to incorporate multiple lidars with complementary field of view (FOV). In essence, we devise a time-synchronized scheme to combine extracted features from separate lidars into a single pointcloud, which is then used to construct a local map and compute the feature-map matching (FMM) coefficients. These coefficients, along with the IMU preinteration observations, are then used to construct a factor graph that will be optimized to produce an estimate of the sliding window trajectory. We also propose a key frame-based map management strategy to marginalize certain poses and pointclouds in the sliding window to grow a global map, which is used to assemble the local map in the later stage. The use of multiple lidars with complementary FOV and the global map ensures that our estimate has low drift and can sustain good localization in situations where single lidar use gives poor result, or even fails to work. Multi-thread computation implementations are also adopted to fractionally cut down the computation time and ensure real-time performance. We demonstrate the efficacy of our system via a series of experiments on public datasets collected from an aerial vehicle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge