MICS : Multi-steps, Inverse Consistency and Symmetric deep learning registration network
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2021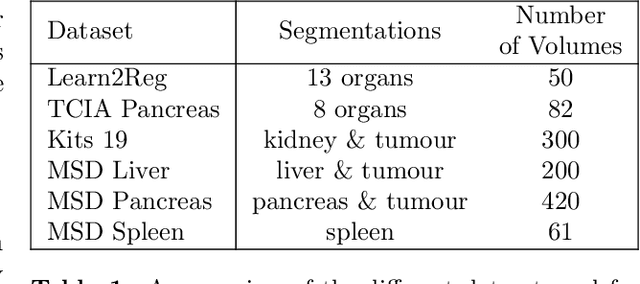
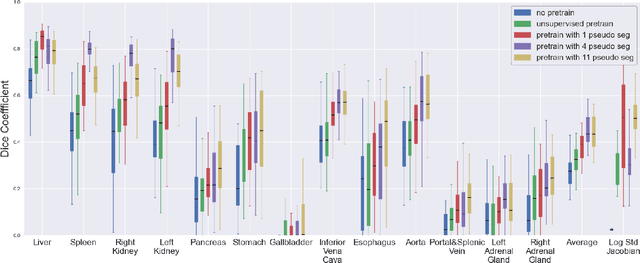
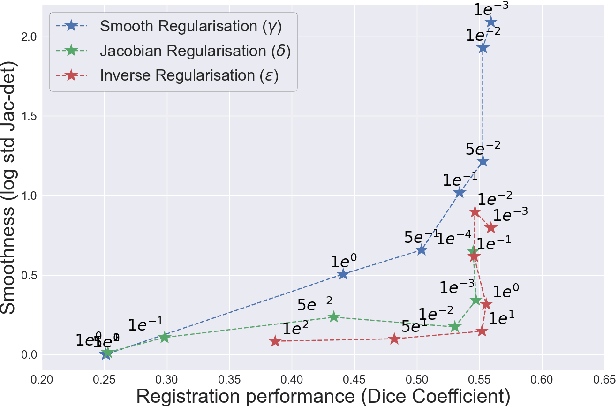
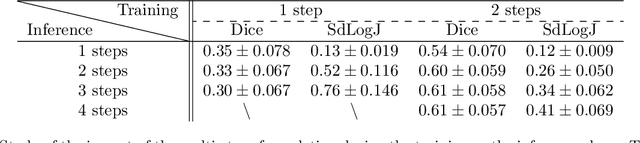
Deformable registration consists of finding the best dense correspondence between two different images. Many algorithms have been published, but the clinical application was made difficult by the high calculation time needed to solve the optimisation problem. Deep learning overtook this limitation by taking advantage of GPU calculation and the learning process. However, many deep learning methods do not take into account desirable properties respected by classical algorithms. In this paper, we present MICS, a novel deep learning algorithm for medical imaging registration. As registration is an ill-posed problem, we focused our algorithm on the respect of different properties: inverse consistency, symmetry and orientation conservation. We also combined our algorithm with a multi-step strategy to refine and improve the deformation grid. While many approaches applied registration to brain MRI, we explored a more challenging body localisation: abdominal CT. Finally, we evaluated our method on a dataset used during the Learn2Reg challenge, allowing a fair comparison with published methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge