Meta-Learning for Online Update of Recommender Systems
Paper and Code
Mar 19, 2022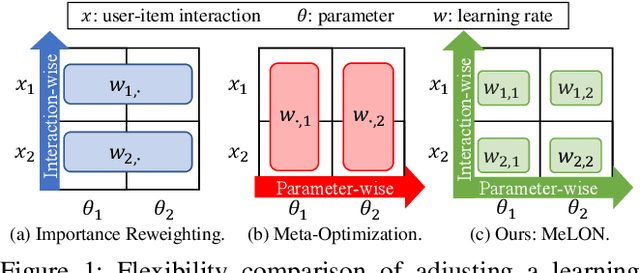
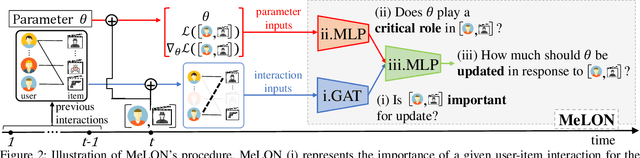
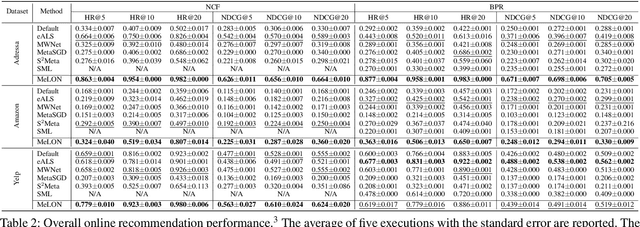
Online recommender systems should be always aligned with users' current interest to accurately suggest items that each user would like. Since user interest usually evolves over time, the update strategy should be flexible to quickly catch users' current interest from continuously generated new user-item interactions. Existing update strategies focus either on the importance of each user-item interaction or the learning rate for each recommender parameter, but such one-directional flexibility is insufficient to adapt to varying relationships between interactions and parameters. In this paper, we propose MeLON, a meta-learning based novel online recommender update strategy that supports two-directional flexibility. It is featured with an adaptive learning rate for each parameter-interaction pair for inducing a recommender to quickly learn users' up-to-date interest. The procedure of MeLON is optimized following a meta-learning approach: it learns how a recommender learns to generate the optimal learning rates for future updates. Specifically, MeLON first enriches the meaning of each interaction based on previous interactions and identifies the role of each parameter for the interaction; and then combines these two pieces of information to generate an adaptive learning rate. Theoretical analysis and extensive evaluation on three real-world online recommender datasets validate the effectiveness of MeLON.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge