Masked LoGoNet: Fast and Accurate 3D Image Analysis for Medical Domain
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2024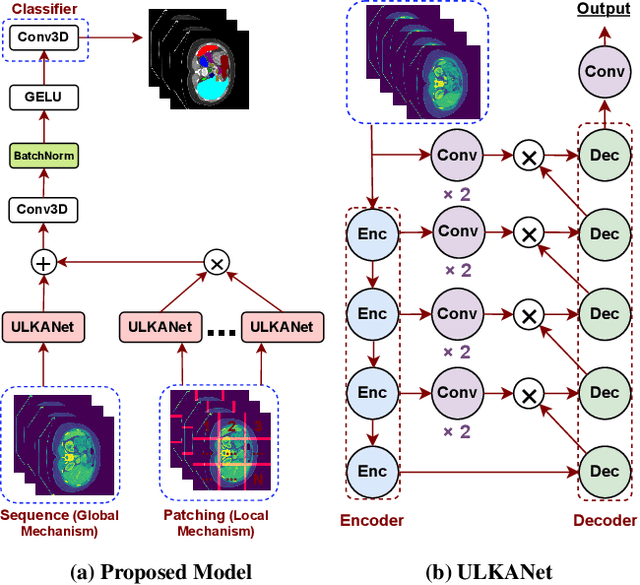
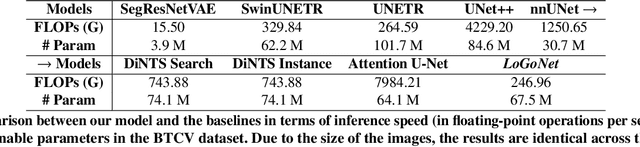
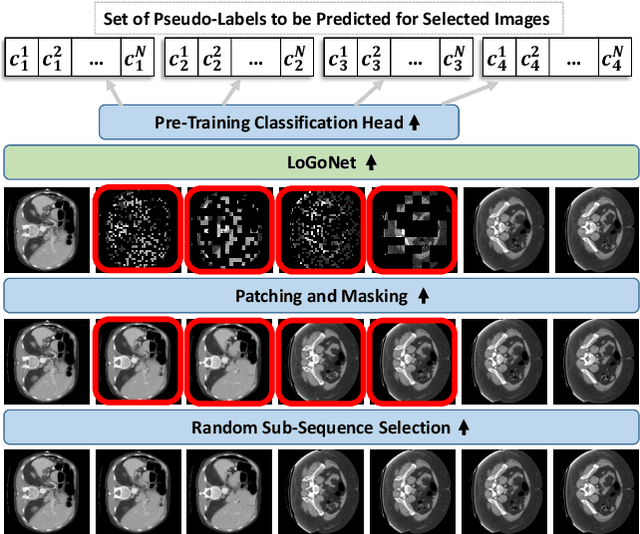
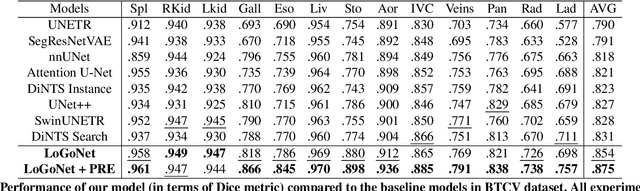
Standard modern machine-learning-based imaging methods have faced challenges in medical applications due to the high cost of dataset construction and, thereby, the limited labeled training data available. Additionally, upon deployment, these methods are usually used to process a large volume of data on a daily basis, imposing a high maintenance cost on medical facilities. In this paper, we introduce a new neural network architecture, termed LoGoNet, with a tailored self-supervised learning (SSL) method to mitigate such challenges. LoGoNet integrates a novel feature extractor within a U-shaped architecture, leveraging Large Kernel Attention (LKA) and a dual encoding strategy to capture both long-range and short-range feature dependencies adeptly. This is in contrast to existing methods that rely on increasing network capacity to enhance feature extraction. This combination of novel techniques in our model is especially beneficial in medical image segmentation, given the difficulty of learning intricate and often irregular body organ shapes, such as the spleen. Complementary, we propose a novel SSL method tailored for 3D images to compensate for the lack of large labeled datasets. The method combines masking and contrastive learning techniques within a multi-task learning framework and is compatible with both Vision Transformer (ViT) and CNN-based models. We demonstrate the efficacy of our methods in numerous tasks across two standard datasets (i.e., BTCV and MSD). Benchmark comparisons with eight state-of-the-art models highlight LoGoNet's superior performance in both inference time and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge