Low Rank Directed Acyclic Graphs and Causal Structure Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2020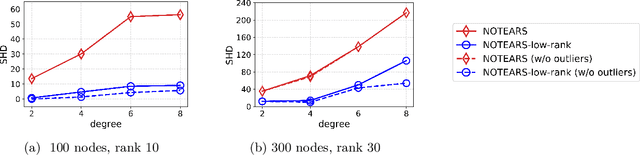
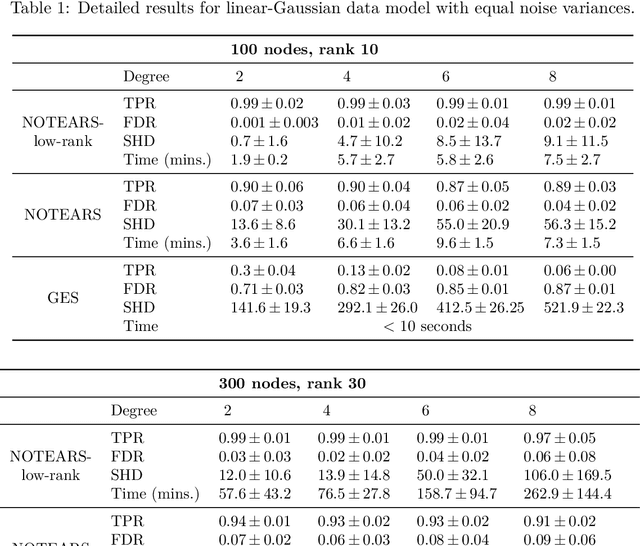
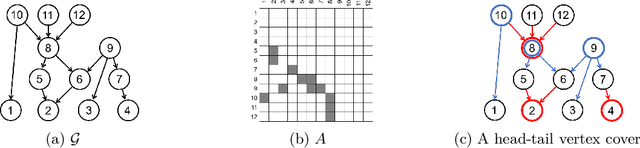
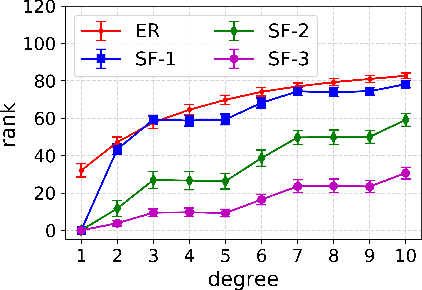
Despite several important advances in recent years, learning causal structures represented by directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) remains a challenging task in high dimensional settings when the graphs to be learned are not sparse. In particular, the recent formulation of structure learning as a continuous optimization problem proved to have considerable advantages over the traditional combinatorial formulation, but the performance of the resulting algorithms is still wanting when the target graph is relatively large and dense. In this paper we propose a novel approach to mitigate this problem, by exploiting a low rank assumption regarding the (weighted) adjacency matrix of a DAG causal model. We establish several useful results relating interpretable graphical conditions to the low rank assumption, and show how to adapt existing methods for causal structure learning to take advantage of this assumption. We also provide empirical evidence for the utility of our low rank algorithms, especially on graphs that are not sparse. Not only do they outperform state-of-the-art algorithms when the low rank condition is satisfied, the performance on randomly generated scale-free graphs is also very competitive even though the true ranks may not be as low as is assumed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge