Localization Coverage Analysis of THz Communication Systems with a 3D Array
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2022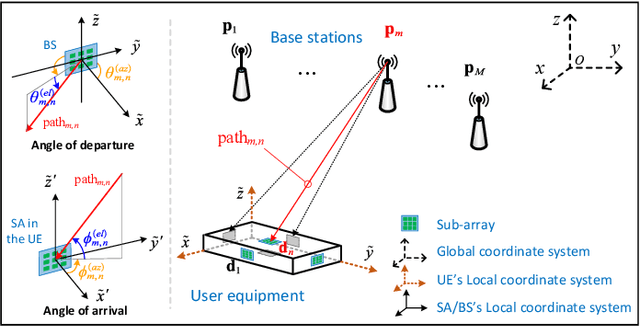
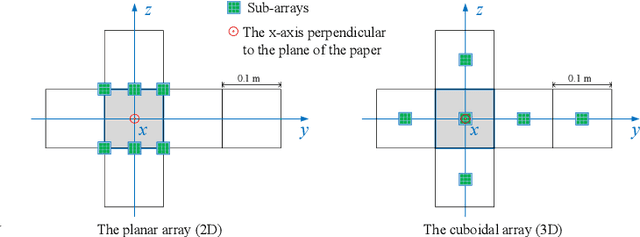
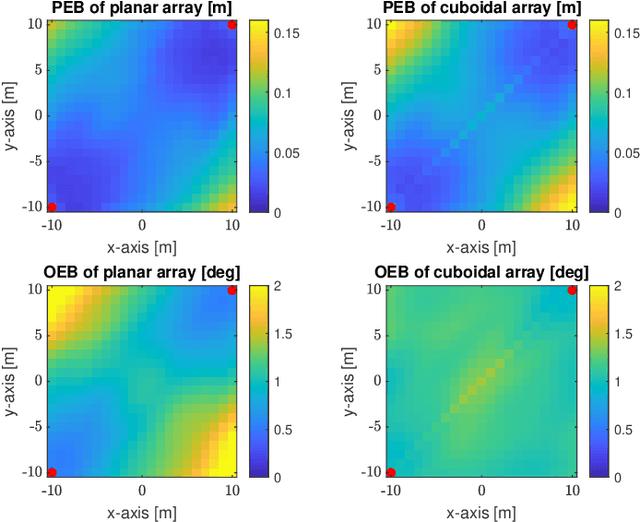
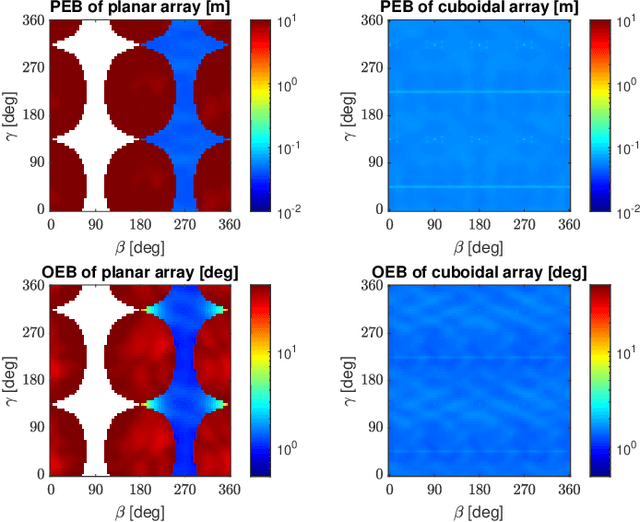
This paper considers the problem of estimating the position and orientation of a user equipped with a three-dimensional (3D) array receiving downlink far-field THz signals from multiple base stations with known positions and orientations. We derive the Cram\'er-Rao Bound for the localization problem and define the coverage of the considered system. We compare the error lower bound distributions of the conventional planar array and the 3D array configurations at different user equipment (UE) positions and orientations. Our numerical results obtained for array configurations with an equal number of elements show very limited coverage of the planar-array configuration, especially across the UE orientation range. Conversely, a 3D array configuration offers an overall higher coverage with minor performance loss in certain UE positions and orientations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge