LLM aided semi-supervision for Extractive Dialog Summarization
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2023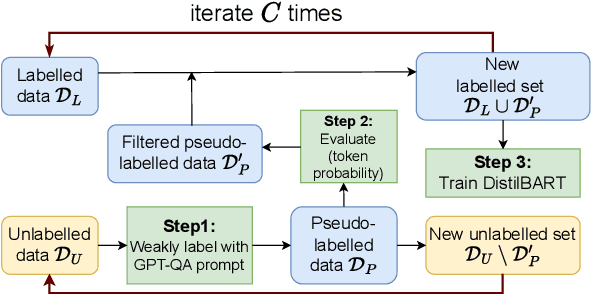
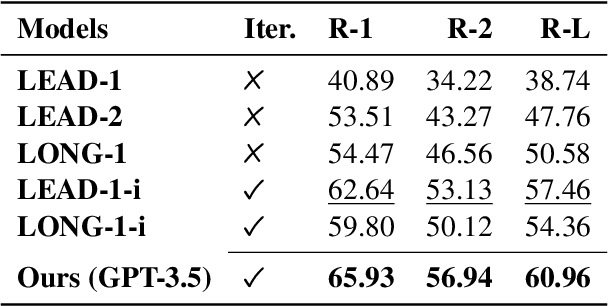
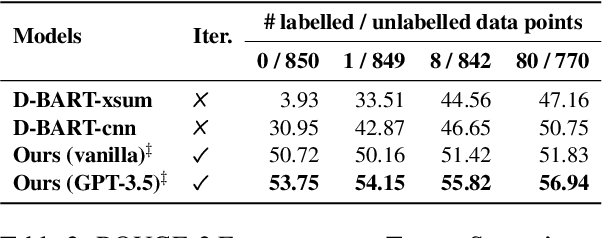

Generating high-quality summaries for chat dialogs often requires large labeled datasets. We propose a method to efficiently use unlabeled data for extractive summarization of customer-agent dialogs. In our method, we frame summarization as a question-answering problem and use state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) to generate pseudo-labels for a dialog. We then use these pseudo-labels to fine-tune a chat summarization model, effectively transferring knowledge from the large LLM into a smaller specialized model. We demonstrate our method on the \tweetsumm dataset, and show that using 10% of the original labelled data set we can achieve 65.9/57.0/61.0 ROUGE-1/-2/-L, whereas the current state-of-the-art trained on the entire training data set obtains 65.16/55.81/64.37 ROUGE-1/-2/-L. In other words, in the worst case (i.e., ROUGE-L) we still effectively retain 94.7% of the performance while using only 10% of the data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge