LESA: Linguistic Encapsulation and Semantic Amalgamation Based Generalised Claim Detection from Online Content
Paper and Code
Jan 28, 2021
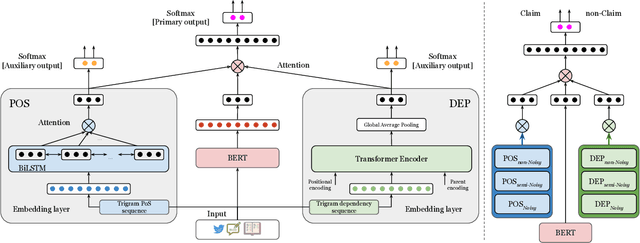
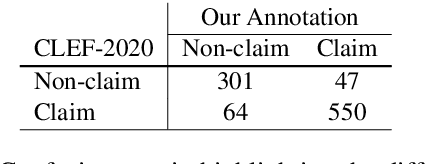

The conceptualization of a claim lies at the core of argument mining. The segregation of claims is complex, owing to the divergence in textual syntax and context across different distributions. Another pressing issue is the unavailability of labeled unstructured text for experimentation. In this paper, we propose LESA, a framework which aims at advancing headfirst into expunging the former issue by assembling a source-independent generalized model that captures syntactic features through part-of-speech and dependency embeddings, as well as contextual features through a fine-tuned language model. We resolve the latter issue by annotating a Twitter dataset which aims at providing a testing ground on a large unstructured dataset. Experimental results show that LESA improves upon the state-of-the-art performance across six benchmark claim datasets by an average of 3 claim-F1 points for in-domain experiments and by 2 claim-F1 points for general-domain experiments. On our dataset too, LESA outperforms existing baselines by 1 claim-F1 point on the in-domain experiments and 2 claim-F1 points on the general-domain experiments. We also release comprehensive data annotation guidelines compiled during the annotation phase (which was missing in the current literature).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge