Learning Visual Conditioning Tokens to Correct Domain Shift for Fully Test-time Adaptation
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2024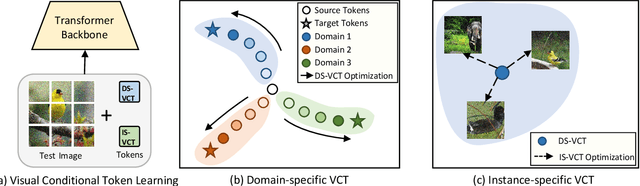
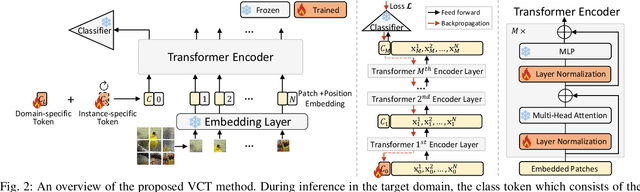
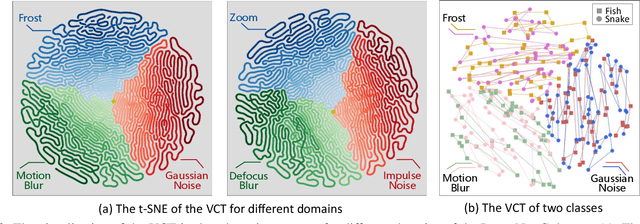
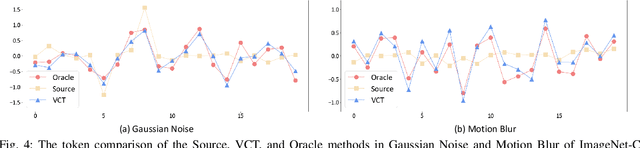
Fully test-time adaptation aims to adapt the network model based on sequential analysis of input samples during the inference stage to address the cross-domain performance degradation problem of deep neural networks. This work is based on the following interesting finding: in transformer-based image classification, the class token at the first transformer encoder layer can be learned to capture the domain-specific characteristics of target samples during test-time adaptation. This learned token, when combined with input image patch embeddings, is able to gradually remove the domain-specific information from the feature representations of input samples during the transformer encoding process, thereby significantly improving the test-time adaptation performance of the source model across different domains. We refer to this class token as visual conditioning token (VCT). To successfully learn the VCT, we propose a bi-level learning approach to capture the long-term variations of domain-specific characteristics while accommodating local variations of instance-specific characteristics. Experimental results on the benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed bi-level visual conditioning token learning method is able to achieve significantly improved test-time adaptation performance by up to 1.9%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge