Learning Spatial-Temporal Graphs for Active Speaker Detection
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2021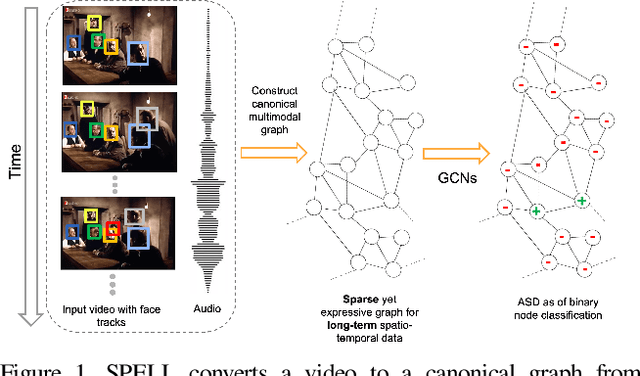
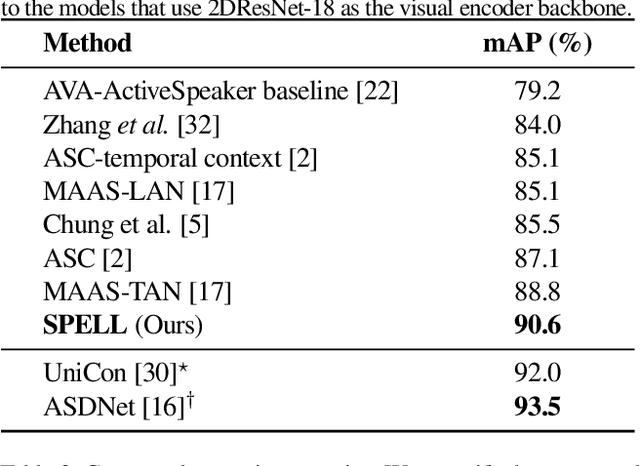
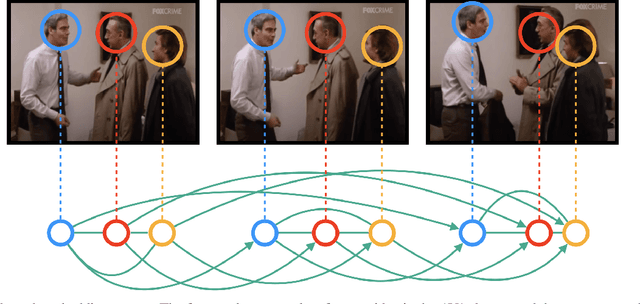
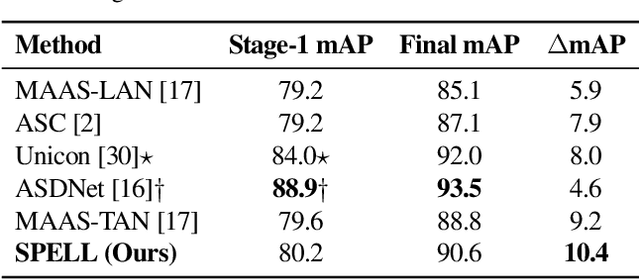
We address the problem of active speaker detection through a new framework, called SPELL, that learns long-range multimodal graphs to encode the inter-modal relationship between audio and visual data. We cast active speaker detection as a node classification task that is aware of longer-term dependencies. We first construct a graph from a video so that each node corresponds to one person. Nodes representing the same identity share edges between them within a defined temporal window. Nodes within the same video frame are also connected to encode inter-person interactions. Through extensive experiments on the Ava-ActiveSpeaker dataset, we demonstrate that learning graph-based representation, owing to its explicit spatial and temporal structure, significantly improves the overall performance. SPELL outperforms several relevant baselines and performs at par with state of the art models while requiring an order of magnitude lower computation cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge