Learning Representations of Instruments for Partial Identification of Treatment Effects
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2024
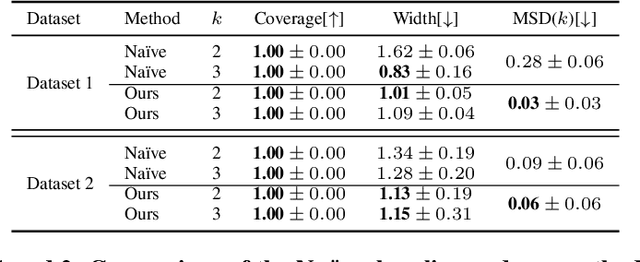
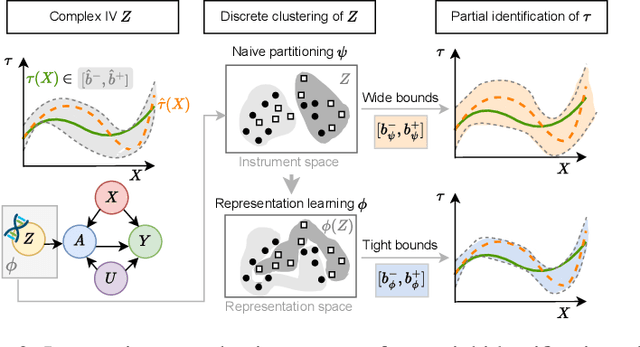
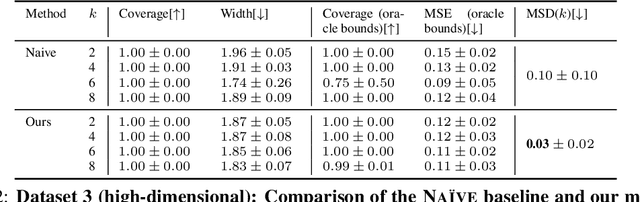
Reliable estimation of treatment effects from observational data is important in many disciplines such as medicine. However, estimation is challenging when unconfoundedness as a standard assumption in the causal inference literature is violated. In this work, we leverage arbitrary (potentially high-dimensional) instruments to estimate bounds on the conditional average treatment effect (CATE). Our contributions are three-fold: (1) We propose a novel approach for partial identification through a mapping of instruments to a discrete representation space so that we yield valid bounds on the CATE. This is crucial for reliable decision-making in real-world applications. (2) We derive a two-step procedure that learns tight bounds using a tailored neural partitioning of the latent instrument space. As a result, we avoid instability issues due to numerical approximations or adversarial training. Furthermore, our procedure aims to reduce the estimation variance in finite-sample settings to yield more reliable estimates. (3) We show theoretically that our procedure obtains valid bounds while reducing estimation variance. We further perform extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness across various settings. Overall, our procedure offers a novel path for practitioners to make use of potentially high-dimensional instruments (e.g., as in Mendelian randomization).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge