Learning Collective Action under Risk Diversity
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2022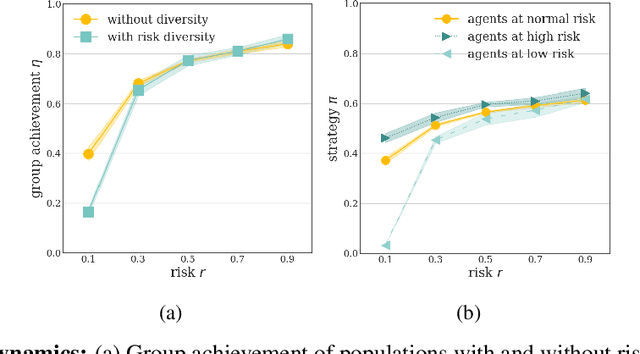
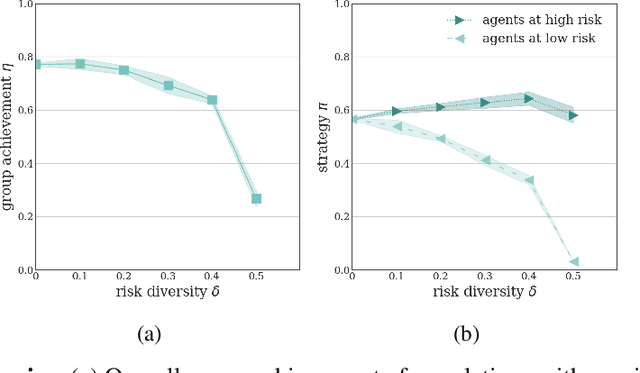
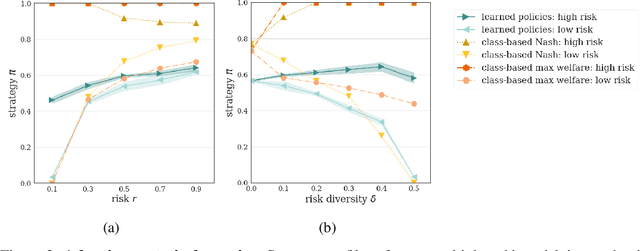
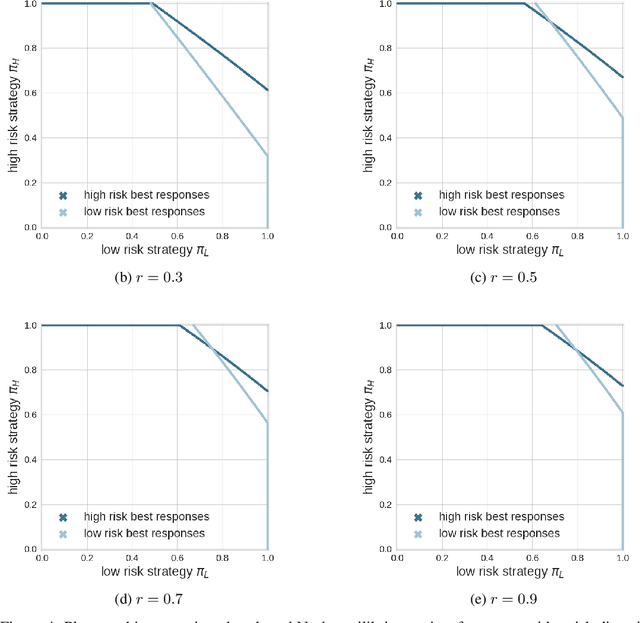
Collective risk dilemmas (CRDs) are a class of n-player games that represent societal challenges where groups need to coordinate to avoid the risk of a disastrous outcome. Multi-agent systems incurring such dilemmas face difficulties achieving cooperation and often converge to sub-optimal, risk-dominant solutions where everyone defects. In this paper we investigate the consequences of risk diversity in groups of agents learning to play CRDs. We find that risk diversity places new challenges to cooperation that are not observed in homogeneous groups. We show that increasing risk diversity significantly reduces overall cooperation and hinders collective target achievement. It leads to asymmetrical changes in agents' policies -- i.e. the increase in contributions from individuals at high risk is unable to compensate for the decrease in contributions from individuals at low risk -- which overall reduces the total contributions in a population. When comparing RL behaviors to rational individualistic and social behaviors, we find that RL populations converge to fairer contributions among agents. Our results highlight the need for aligning risk perceptions among agents or develop new learning techniques that explicitly account for risk diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge