Knowing what you know in brain segmentation using deep neural networks
Paper and Code
Dec 18, 2018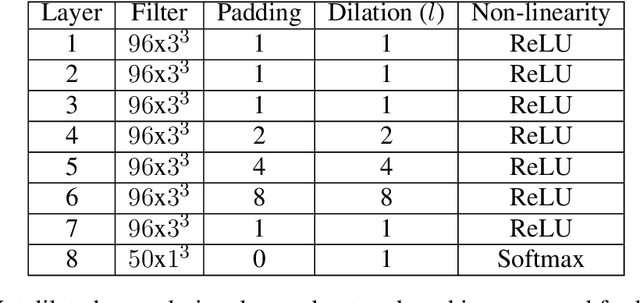
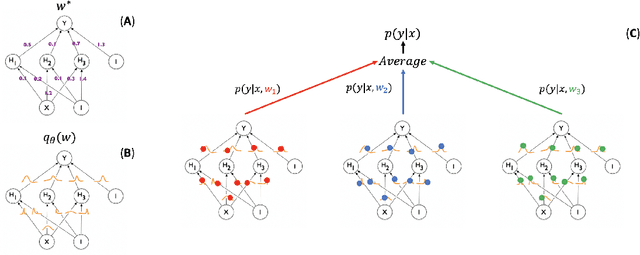
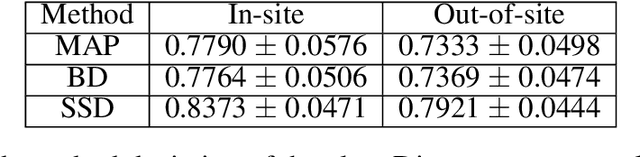
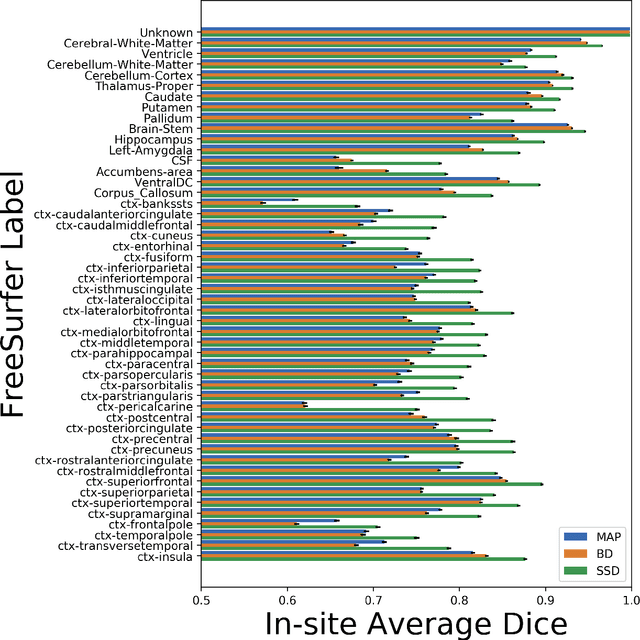
In this paper, we describe a deep neural network trained to predict FreeSurfer segmentations of structural MRI volumes, in seconds rather than hours. The network was trained and evaluated on an extremely large dataset (n = 11,148), obtained by combining data from more than a hundred sites. We also show that the prediction uncertainty of the network at each voxel is a good indicator of whether the network has made an error. The resulting uncertainty volume can be used in conjunction with the predicted segmentation to improve downstream uses, such as calculation of measures derived from segmentation regions of interest or the building of prediction models. Finally, we demonstrate that the average prediction uncertainty across voxels in the brain is an excellent indicator of manual quality control ratings, outperforming the best available automated solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge