KGRGRL: A User's Permission Reasoning Method Based on Knowledge Graph Reward Guidance Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
May 16, 2022
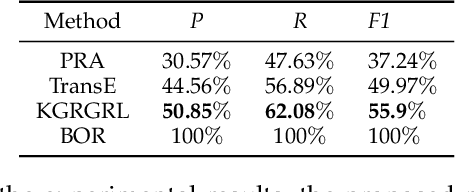
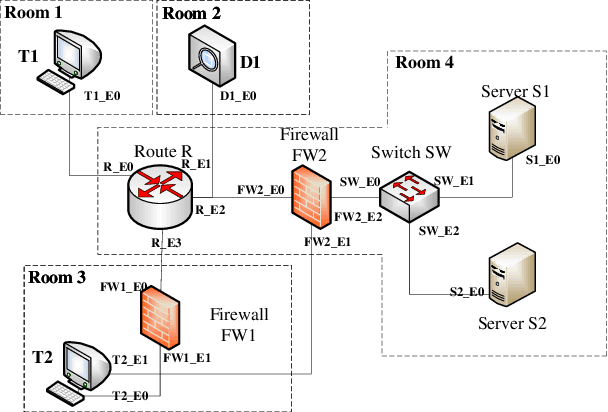
In general, multiple domain cyberspace security assessments can be implemented by reasoning user's permissions. However, while existing methods include some information from the physical and social domains, they do not provide a comprehensive representation of cyberspace. Existing reasoning methods are also based on expert-given rules, resulting in inefficiency and a low degree of intelligence. To address this challenge, we create a Knowledge Graph (KG) of multiple domain cyberspace in order to provide a standard semantic description of the multiple domain cyberspace. Following that, we proposed a user's permissions reasoning method based on reinforcement learning. All permissions in cyberspace are represented as nodes, and an agent is trained to find all permissions that user can have according to user's initial permissions and cyberspace KG. We set 10 reward setting rules based on the features of cyberspace KG in the reinforcement learning of reward information setting, so that the agent can better locate user's all permissions and avoid blindly finding user's permissions. The results of the experiments showed that the proposed method can successfully reason about user's permissions and increase the intelligence level of the user's permissions reasoning method. At the same time, the F1 value of the proposed method is 6% greater than that of the Translating Embedding (TransE) method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge