KALM: Knowledge-Aware Integration of Local, Document, and Global Contexts for Long Document Understanding
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2022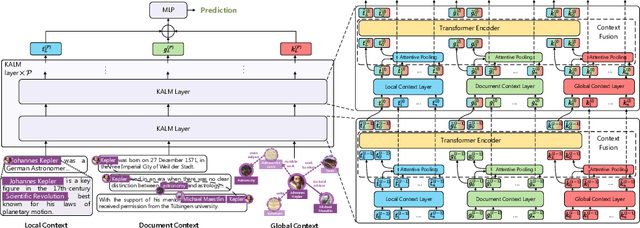
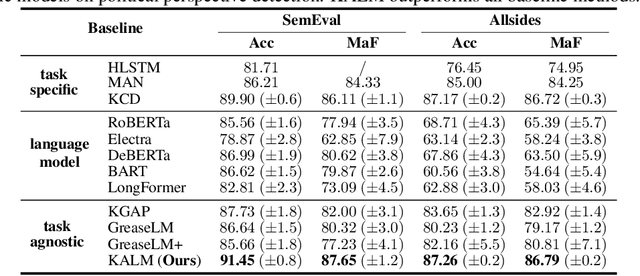
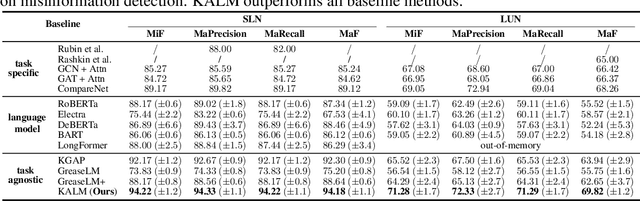
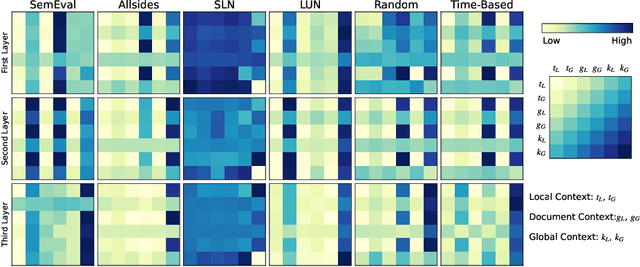
With the advent of pre-trained language models (LMs), increasing research efforts have been focusing on infusing commonsense and domain-specific knowledge to prepare LMs for downstream tasks. These works attempt to leverage knowledge graphs, the de facto standard of symbolic knowledge representation, along with pre-trained LMs. While existing approaches leverage external knowledge, it remains an open question how to jointly incorporate knowledge graphs representing varying contexts, from local (e.g., sentence), to document-level, to global knowledge, to enable knowledge-rich and interpretable exchange across these contexts. Such rich contextualization can be especially beneficial for long document understanding tasks since standard pre-trained LMs are typically bounded by the input sequence length. In light of these challenges, we propose KALM, a Knowledge-Aware Language Model that jointly leverages knowledge in local, document-level, and global contexts for long document understanding. KALM first encodes long documents and knowledge graphs into the three knowledge-aware context representations. It then processes each context with context-specific layers, followed by a context fusion layer that facilitates interpretable knowledge exchange to derive an overarching document representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that KALM achieves state-of-the-art performance on three long document understanding tasks across 6 datasets/settings. Further analyses reveal that the three knowledge-aware contexts are complementary and they all contribute to model performance, while the importance and information exchange patterns of different contexts vary with respect to different tasks and datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge