Interrogating LLM design under a fair learning doctrine
Paper and Code
Feb 22, 2025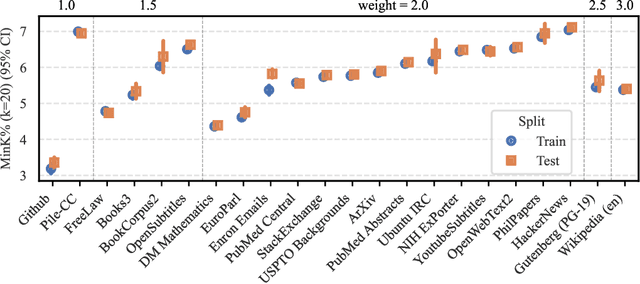
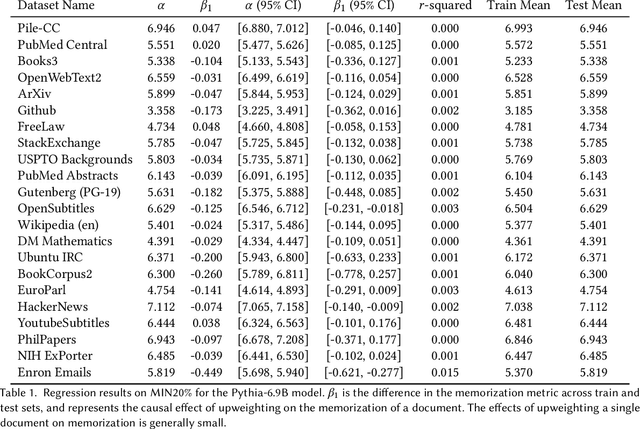
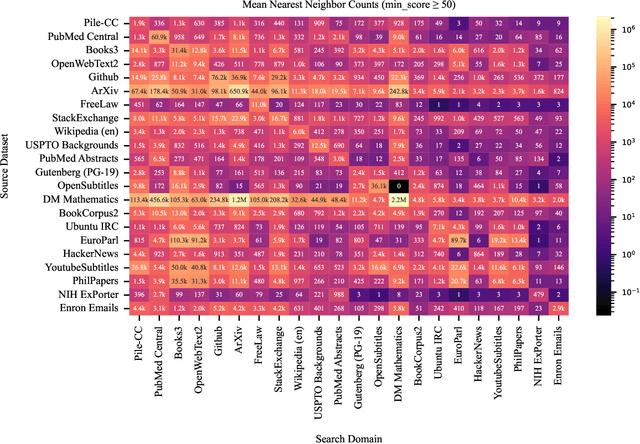
The current discourse on large language models (LLMs) and copyright largely takes a "behavioral" perspective, focusing on model outputs and evaluating whether they are substantially similar to training data. However, substantial similarity is difficult to define algorithmically and a narrow focus on model outputs is insufficient to address all copyright risks. In this interdisciplinary work, we take a complementary "structural" perspective and shift our focus to how LLMs are trained. We operationalize a notion of "fair learning" by measuring whether any training decision substantially affected the model's memorization. As a case study, we deconstruct Pythia, an open-source LLM, and demonstrate the use of causal and correlational analyses to make factual determinations about Pythia's training decisions. By proposing a legal standard for fair learning and connecting memorization analyses to this standard, we identify how judges may advance the goals of copyright law through adjudication. Finally, we discuss how a fair learning standard might evolve to enhance its clarity by becoming more rule-like and incorporating external technical guidelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge