Interpreting BERT-based Text Similarity via Activation and Saliency Maps
Paper and Code
Aug 13, 2022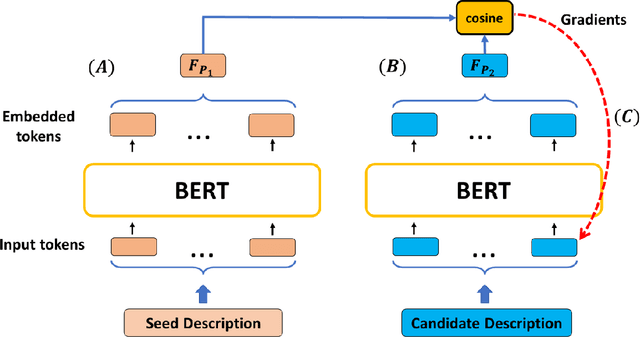
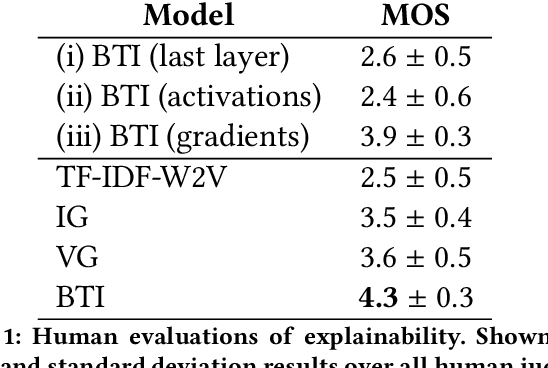
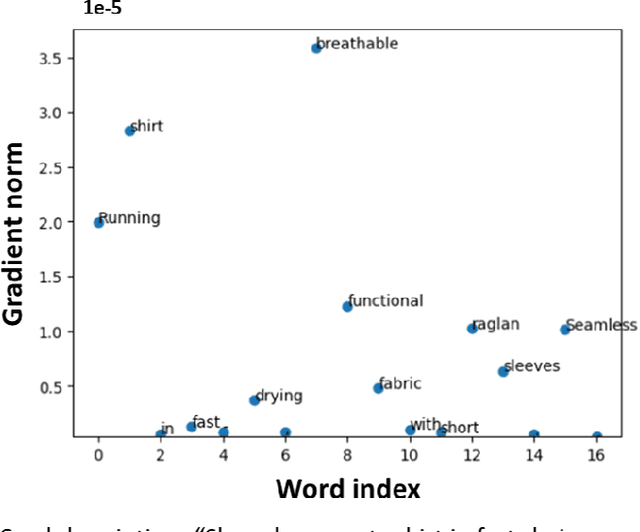
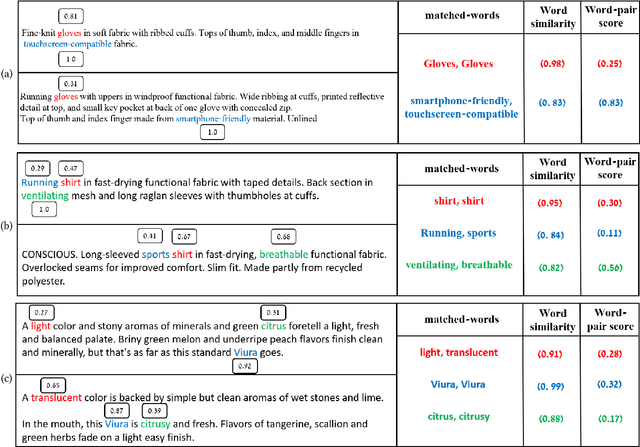
Recently, there has been growing interest in the ability of Transformer-based models to produce meaningful embeddings of text with several applications, such as text similarity. Despite significant progress in the field, the explanations for similarity predictions remain challenging, especially in unsupervised settings. In this work, we present an unsupervised technique for explaining paragraph similarities inferred by pre-trained BERT models. By looking at a pair of paragraphs, our technique identifies important words that dictate each paragraph's semantics, matches between the words in both paragraphs, and retrieves the most important pairs that explain the similarity between the two. The method, which has been assessed by extensive human evaluations and demonstrated on datasets comprising long and complex paragraphs, has shown great promise, providing accurate interpretations that correlate better with human perceptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge