Image Restoration by Deep Projected GSURE
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2021
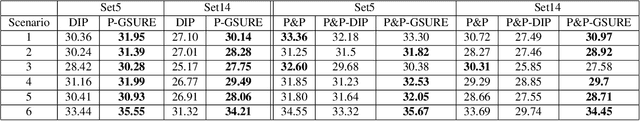

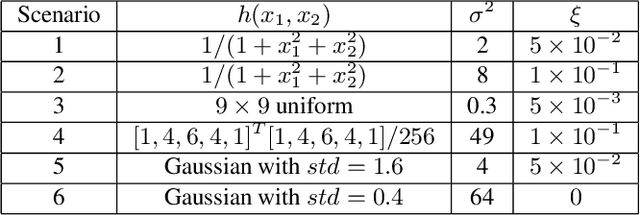
Ill-posed inverse problems appear in many image processing applications, such as deblurring and super-resolution. In recent years, solutions that are based on deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown great promise. Yet, most of these techniques, which train CNNs using external data, are restricted to the observation models that have been used in the training phase. A recent alternative that does not have this drawback relies on learning the target image using internal learning. One such prominent example is the Deep Image Prior (DIP) technique that trains a network directly on the input image with a least-squares loss. In this paper, we propose a new image restoration framework that is based on minimizing a loss function that includes a "projected-version" of the Generalized SteinUnbiased Risk Estimator (GSURE) and parameterization of the latent image by a CNN. We demonstrate two ways to use our framework. In the first one, where no explicit prior is used, we show that the proposed approach outperforms other internal learning methods, such as DIP. In the second one, we show that our GSURE-based loss leads to improved performance when used within a plug-and-play priors scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge