Hybrid Random Features
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2021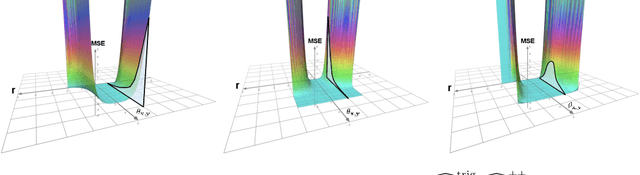
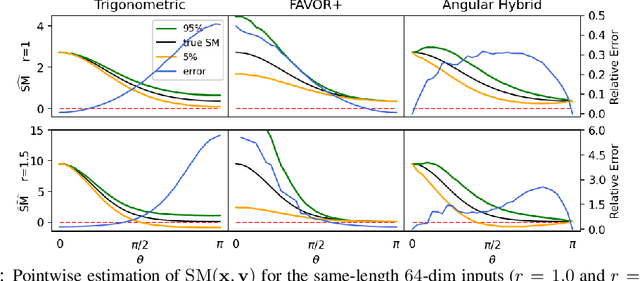
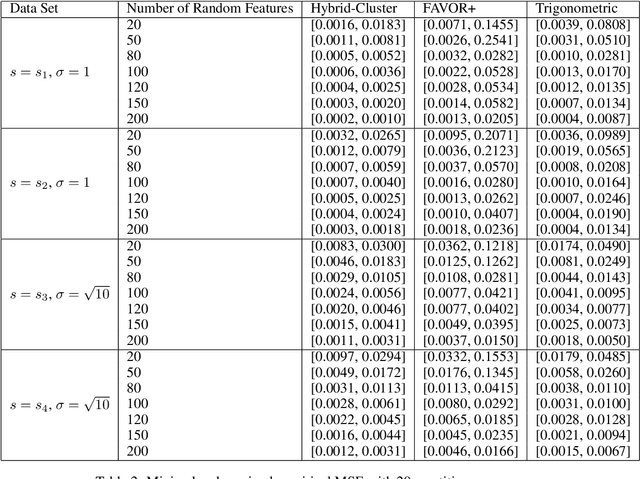
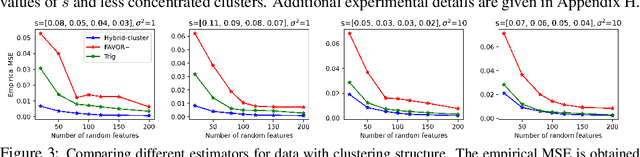
We propose a new class of random feature methods for linearizing softmax and Gaussian kernels called hybrid random features (HRFs) that automatically adapt the quality of kernel estimation to provide most accurate approximation in the defined regions of interest. Special instantiations of HRFs lead to well-known methods such as trigonometric (Rahimi and Recht, 2007) or (recently introduced in the context of linear-attention Transformers) positive random features (Choromanski et al., 2021). By generalizing Bochner's Theorem for softmax/Gaussian kernels and leveraging random features for compositional kernels, the HRF-mechanism provides strong theoretical guarantees - unbiased approximation and strictly smaller worst-case relative errors than its counterparts. We conduct exhaustive empirical evaluation of HRF ranging from pointwise kernel estimation experiments, through tests on data admitting clustering structure to benchmarking implicit-attention Transformers (also for downstream Robotics applications), demonstrating its quality in a wide spectrum of machine learning problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge