How Robust is your Fair Model? Exploring the Robustness of Diverse Fairness Strategies
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2022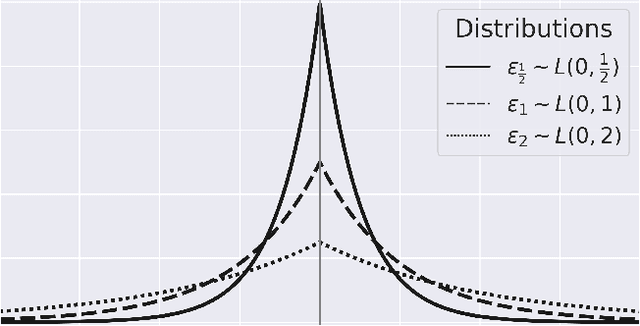
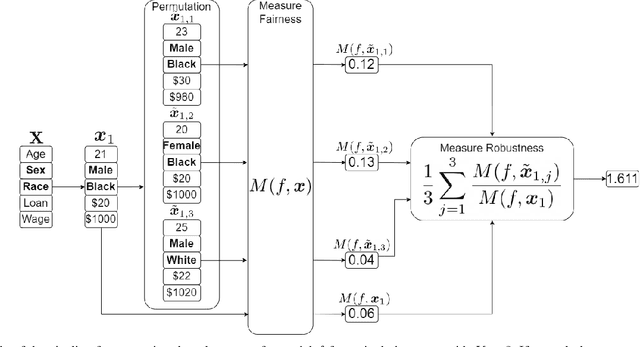
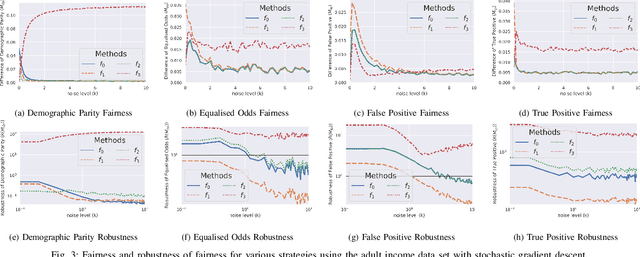
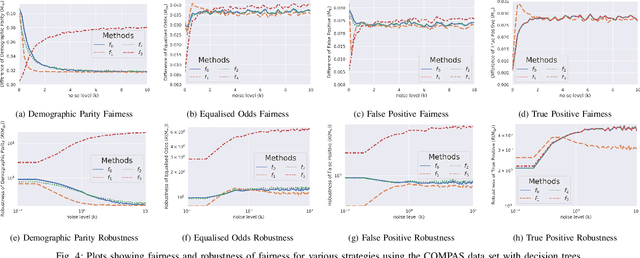
With the introduction of machine learning in high-stakes decision making, ensuring algorithmic fairness has become an increasingly important problem to solve. In response to this, many mathematical definitions of fairness have been proposed, and a variety of optimisation techniques have been developed, all designed to maximise a defined notion of fairness. However, fair solutions are reliant on the quality of the training data, and can be highly sensitive to noise. Recent studies have shown that robustness (the ability for a model to perform well on unseen data) plays a significant role in the type of strategy that should be used when approaching a new problem and, hence, measuring the robustness of these strategies has become a fundamental problem. In this work, we therefore propose a new criterion to measure the robustness of various fairness optimisation strategies - the robustness ratio. We conduct multiple extensive experiments on five bench mark fairness data sets using three of the most popular fairness strategies with respect to four of the most popular definitions of fairness. Our experiments empirically show that fairness methods that rely on threshold optimisation are very sensitive to noise in all the evaluated data sets, despite mostly outperforming other methods. This is in contrast to the other two methods, which are less fair for low noise scenarios but fairer for high noise ones. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to quantitatively evaluate the robustness of fairness optimisation strategies. This can potentially can serve as a guideline in choosing the most suitable fairness strategy for various data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge